rTMS over the human medial parietal cortex impairs online reaching corrections
- PMID: 38141108
- PMCID: PMC10917872
- DOI: 10.1007/s00429-023-02735-7
rTMS over the human medial parietal cortex impairs online reaching corrections
Abstract
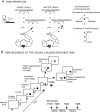
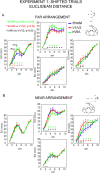
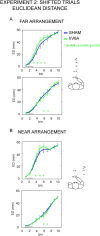
Indirect correlational evidence suggests that the posteromedial sector of the human parietal cortex (area hV6A) is involved in reaching corrections. We interfered with hV6A functions using repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) while healthy participants performed reaching movements and in-flight adjustments of the hand trajectory in presence of unexpected target shifts. rTMS over hV6A specifically altered action reprogramming, causing deviations of the shifted trajectories, particularly along the vertical dimension (i.e., distance). This study provides evidence of the functional relevance of hV6A in action reprogramming while a sudden event requires a change in performance and shows that hV6A also plays a role in state estimation during reaching. These findings are in line with neurological data showing impairments in actions performed along the distance dimension when lesions occur in the dorsal posterior parietal cortex.
Keywords: Area V6A; Correction of reach direction and position; Human brain; Limb state estimation; Posterior parietal cortex.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Short Route for Reach Planning between Human V6A and the Motor Cortex.J Neurosci. 2023 Mar 22;43(12):2116-2125. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1609-22.2022. Epub 2023 Feb 14. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36788027 Free PMC article.
-
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Over the Human Medial Posterior Parietal Cortex Disrupts Depth Encoding During Reach Planning.Cereb Cortex. 2021 Jan 1;31(1):267-280. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaa224. Cereb Cortex. 2021. PMID: 32995831
-
Complementary contribution of the medial and lateral human parietal cortex to grasping: a repetitive TMS study.Cereb Cortex. 2023 Apr 25;33(9):5122-5134. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhac404. Cereb Cortex. 2023. PMID: 36245221 Free PMC article.
-
Visually-guided correction of hand reaching movements: The neurophysiological bases in the cerebral cortex.Vision Res. 2015 May;110(Pt B):244-56. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2014.09.009. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Vision Res. 2015. PMID: 25264945 Review.
-
The posterior parietal area V6A: An attentionally-modulated visuomotor region involved in the control of reach-to-grasp action.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Oct;141:104823. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104823. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 35961383 Review.
Cited by
-
Sensorimotor environment but not task rule reconfigures population dynamics in rhesus monkey posterior parietal cortex.Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 3;16(1):1116. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56360-5. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39900579 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of aSPOC in the Online Updating of Reach-to-Grasp to Mechanical Perturbations of Hand Transport.J Neurosci. 2025 Mar 19;45(12):e0173242025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0173-24.2025. J Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39870529
-
Role of the Medial Posterior Parietal Cortex in Orchestrating Attention and Reaching.J Neurosci. 2025 Jan 1;45(1):e0659242024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0659-24.2024. J Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39500577 Free PMC article.
-
iTBS over the left hV6A enhances PPC-PPC functional connectivity during reaching tasks: an EEG study.Front Neurosci. 2025 Mar 26;19:1536308. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1536308. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40242457 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

