The Essential Functions of Molecular Chaperones and Folding Enzymes in Maintaining Endoplasmic Reticulum Homeostasis
- PMID: 38143019
- PMCID: PMC12015986
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168418
The Essential Functions of Molecular Chaperones and Folding Enzymes in Maintaining Endoplasmic Reticulum Homeostasis
Abstract
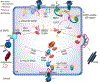
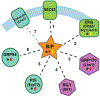
It has been estimated that up to one-third of the proteins encoded by the human genome enter the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) as extended polypeptide chains where they undergo covalent modifications, fold into their native structures, and assemble into oligomeric protein complexes. The fidelity of these processes is critical to support organellar, cellular, and organismal health, and is perhaps best underscored by the growing number of disease-causing mutations that reduce the fidelity of protein biogenesis in the ER. To meet demands encountered by the diverse protein clientele that mature in the ER, this organelle is populated with a cadre of molecular chaperones that prevent protein aggregation, facilitate protein disulfide isomerization, and lower the activation energy barrier of cis-trans prolyl isomerization. Components of the lectin (glycan-binding) chaperone system also reside within the ER and play numerous roles during protein biogenesis. In addition, the ER houses multiple homologs of select chaperones that can recognize and act upon diverse peptide signatures. Moreover, redundancy helps ensure that folding-compromised substrates are unable to overwhelm essential ER-resident chaperones and enzymes. In contrast, the ER in higher eukaryotic cells possesses a single member of the Hsp70, Hsp90, and Hsp110 chaperone families, even though several homologs of these molecules reside in the cytoplasm. In this review, we discuss specific functions of the many factors that maintain ER quality control, highlight some of their interactions, and describe the vulnerabilities that arise from the absence of multiple members of some chaperone families.
Keywords: chaperones; co-chaperones; protein folding; proteostasis; unfolded protein response (UPR).
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Excess dietary sodium restores electrolyte and water homeostasis caused by loss of the endoplasmic reticulum molecular chaperone, GRP170, in the mouse nephron.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025 Feb 1;328(2):F173-F189. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00192.2024. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39556479 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Scaffold Hopping and Screening for Potent Small Molecule Agonists for GRP94: Implications to Alleviate ER Stress-Associated Pathogenesis.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Apr;66(4):737-755. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00685-3. Epub 2023 Feb 10. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 36763304
-
Protein-rich foods, sea foods, and gut microbiota amplify immune responses in chronic diseases and cancers - Targeting PERK as a novel therapeutic strategy for chronic inflammatory diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Mar;255:108604. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2024.108604. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38360205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-chaperones fine-tune the function of heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70), whether to fold, hold, or degrade substrates in ensuring cellular protein homeostasis.J Biosci. 2025;50:48. J Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40536193 Review.
Cited by
-
Conformational plasticity of a BiP-GRP94 chaperone complex.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025 Jul 14. doi: 10.1038/s41594-025-01619-0. Online ahead of print. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40659993
-
The structural and functional dynamics of BiP and Grp94: opportunities for therapeutic discovery.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2025 May;46(5):453-467. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2025.03.004. Epub 2025 Apr 18. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40253284 Review.
-
Excess dietary sodium partially restores salt and water homeostasis caused by loss of the endoplasmic reticulum molecular chaperone, GRP170, in the mouse nephron.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 14:2024.01.13.575426. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.13.575426. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025 Feb 01;328(2):F173-F189. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00192.2024. PMID: 38260467 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Targeting stress induction of GRP78 by cardiac glycoside oleandrin dually suppresses cancer and COVID-19.Cell Biosci. 2024 Sep 6;14(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01297-3. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39238058 Free PMC article.
-
The prolyl isomerase FKBP11 is a secretory translocon accessory factor.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Nov 1;35(11):ar135. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-07-0305. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39259761 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

