Case report: XMEN disease: a patient with recurrent Hodgkin lymphoma and immune thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 38143450
- PMCID: PMC10740371
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1264329
Case report: XMEN disease: a patient with recurrent Hodgkin lymphoma and immune thrombocytopenia
Abstract
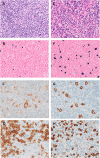
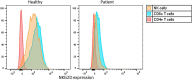
Here we present the case of a 28-year-old man with X-linked immunodeficiency with magnesium defect, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection and neoplasia (XMEN) disease. He presented with immune thrombocytopenia within 1 year after successful autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for recurrent EBV-associated classical Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL). The combination of EBV- associated malignancy, autoimmunity, recurrent airway infections at young age and bronchiectasis, prompted immunological investigation for an inborn error of immunity (IEI). Genetic testing revealed XMEN disease. XMEN disease is characterized by a glycosylation defect due to mutations in the MAGT1 gene. Germline mutations in the MAGT1 gene disrupt glycosylation of the NKG2D receptor in immune cells, including natural killer and CD8-positive T cells, vital for immune surveillance, especially against EBV. Consequently, individuals with XMEN disease, are prone to EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disorders in addition to auto-immunity. Early recognition of adult onset IEI-related B-lymphoproliferative disorders, including CHL is of vital importance for treatment decisions, including (allogeneic) haematopoietic stem cell transplantation and family screening.
Keywords: Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL); XMEN disease; hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; immune thrombocytopenia (ITP); inborn error of immunity.
Copyright © 2023 de Groot, Kwakernaak, van Leeuwen, van Spaendonk, Kooi, de Jong, Kuijpers, Zijlstra and de Bree.
Conflict of interest statement
GB had a grant from Takeda paid through her institution. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the american college of medical genetics and genomics and the association for molecular pathology. Genet Med. (2015) 17:405–24. 10.1038/gim.2015.30 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

