Incidence of injury and illness among paediatric Team USA athletes competing in the 2020 Tokyo and 2022 Beijing Olympic and Paralympic Games
- PMID: 38143720
- PMCID: PMC10749061
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjsem-2023-001730
Incidence of injury and illness among paediatric Team USA athletes competing in the 2020 Tokyo and 2022 Beijing Olympic and Paralympic Games
Abstract
Objective: To describe the incidence of injuries and illnesses among paediatric Team USA athletes competing in the Tokyo 2020 Olympic and Paralympic Games, and the 2022 Beijing Olympic and Paralympic Games.
Methods: An electronic medical record system documented all injuries and illnesses that occurred while competing in the four Games periods. Incidence (IR) with 95% CI per 1000 athlete days were calculated for both injuries and illnesses. Incidence rate ratios (IRR) were calculated to compare injury and illness rates based on age (paediatric vs non-paediatric) sex, Games period and sport type.
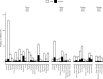
Results: Two hundred paediatric athletes (age range, 15-21 years) competed across the four Games periods, representing 16.1% of all Team USA athletes. The overall injury IR (95% CI) was 13.4 (9.8 to 18.1), and the overall illness IR was 5.5 (3.3 to 8.7). There were no differences in incidence between paediatric and non-paediatric athletes for either injury (IRR (95% CI): 0.9 (0.6 to 1.2)) or illness (IRR (95% CI): 0.9 (0.5 to 1.5)). Female paediatric athletes were more likely to sustain an injury compared with male paediatric athletes (IRR (95% CI): 2.4 (1.1 to 5.3)). The most common mechanism of injury was gradual onset (IR, 4.3 (2.3 to 7.2)), and injuries most commonly occurred during practices (IR, 7.0 (4.5 to 10.5)).
Conclusion: Paediatric athletes account for a substantial proportion of Team USA athletes. It is essential that paediatric sports medicine experts are included in the medical team given that paediatric Team USA athletes are just as likely as their adult teammates to sustain an injury or illness.
Keywords: Adolescent; Epidemiology; Olympics; Para-Athletes.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Kerr ZY, Comstock RD, Dompier TP, et al. The first decade of web-based sports injury surveillance (2004-2005 through 2013-2014): methods of the national collegiate athletic association injury surveillance program and high school reporting information online. J Athl Train 2018;53:729–37. 10.4085/1062-6050-143-17 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources