Magnetic properties of Fe-doped NiO nanoparticles
- PMID: 38144307
- PMCID: PMC10746408
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22876
Magnetic properties of Fe-doped NiO nanoparticles
Abstract
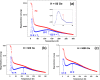
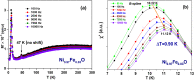
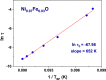
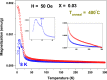
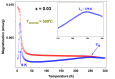
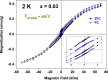
Undoped and Fe-doped NiO nanoparticles were successfully synthesized using a lyophilization method and systematically characterized through magnetization techniques over a wide temperature range, with varying intensity and frequency of the applied magnetic fields. The Ni1-xFexO nanoparticles can be described by a core-shell model, which reveals that Fe doping enhances exchange interactions in correlation with nanoparticle size reduction. The nanoparticles exhibit a superparamagnetic blocking transition, primarily attributed to their cores, at temperatures ranging from above room temperature to low temperatures, depending on the Fe-doping level and sample synthesis temperature. The nanoparticle shells also exhibit a transition at low temperatures, in this case to a cluster-glass-like state, caused by the dipolar magnetic interactions between the net magnetic moments of the clusters. Their freezing temperature shifts to higher temperatures as the Fe-doping level increases. The existence of an exchange bias interaction was observed, thus validating the core-shell model proposed.
Keywords: Cluster-glass; Core-shell model; Fe-doped; Nanoparticles; Nickel oxide; Spin-glass.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







References
-
- Tadic M., Nikolic D., Panjan M., Blake G.R. Magnetic properties of NiO (nickel oxide) nanoparticles: blocking temperature and Neel temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2015;647:1061–1068. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.06.027. - DOI
-
- Nikolić D., Panjan M., Blake G.R., Tadić M. Annealing-dependent structural and magnetic properties of nickel oxide (NiO) nanoparticles in a silica matrix. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015;35:3843–3852. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.06.024. - DOI
-
- Winkler E., Zysler R.D., Mansilla M.V., Fiorani D. Surface anisotropy effects in NiO nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B. 2005;72 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.72.132409. - DOI
-
- L. Néel, Théorie du traînage magnétique des ferromagnétiques en grains fins avec application aux terres cuites, Ann. Geophys.(149AD) 99–136. https://hal.science/hal-03070532 (accessed February 6, 2023).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

