The Global Impact of COVID-19: Historical Development, Molecular Characterization, Drug Discovery and Future Directions
- PMID: 38144436
- PMCID: PMC10748929
- DOI: 10.1177/2632010X231218075
The Global Impact of COVID-19: Historical Development, Molecular Characterization, Drug Discovery and Future Directions
Abstract
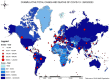
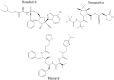
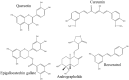
In December 2019, an outbreak of a respiratory disease called the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by a new coronavirus known as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) began in Wuhan, China. The SARS-CoV-2, an encapsulated positive-stranded RNA virus, spread worldwide with disastrous consequences for people's health, economies, and quality of life. The disease has had far-reaching impacts on society, including economic disruption, school closures, and increased stress and anxiety. It has also highlighted disparities in healthcare access and outcomes, with marginalized communities disproportionately affected by the SARS-CoV-2. The symptoms of COVID-19 range from mild to severe. There is presently no effective cure. Nevertheless, significant progress has been made in developing COVID-19 vaccine for different therapeutic targets. For instance, scientists developed multifold vaccine candidates shortly after the COVID-19 outbreak after Pfizer and AstraZeneca discovered the initial COVID-19 vaccines. These vaccines reduce disease spread, severity, and mortality. The addition of rapid diagnostics to microscopy for COVID-19 diagnosis has proven crucial. Our review provides a thorough overview of the historical development of COVID-19 and molecular and biochemical characterization of the SARS-CoV-2. We highlight the potential contributions from insect and plant sources as anti-SARS-CoV-2 and present directions for future research.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; drug discovery; epidemiology; insects; plants.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Consensus summary report for CEPI/BC March 12-13, 2020 meeting: Assessment of risk of disease enhancement with COVID-19 vaccines.Vaccine. 2020 Jun 26;38(31):4783-4791. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.05.064. Epub 2020 May 25. Vaccine. 2020. PMID: 32507409 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress and challenges in drug development against COVID-19 coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) - an update on the status.Infect Genet Evol. 2020 Sep;83:104327. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104327. Epub 2020 Apr 19. Infect Genet Evol. 2020. PMID: 32320825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Immunological Review of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Vaccine Serology: Innate and Adaptive Responses to mRNA, Adenovirus, Inactivated and Protein Subunit Vaccines.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Dec 26;11(1):51. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11010051. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36679897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of the Progress and Challenges of Developing a Vaccine for COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 14;11:585354. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.585354. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33163000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The outbreak of the novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): A review of the current global status.J Infect Public Health. 2020 Nov;13(11):1601-1610. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.011. Epub 2020 Aug 4. J Infect Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32778421 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

