P-Glycoprotein Exacerbates Brain Injury Following Experimental Cerebral Ischemia by Promoting Proinflammatory Microglia Activation
- PMID: 38144707
- PMCID: PMC10748718
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/6916819
P-Glycoprotein Exacerbates Brain Injury Following Experimental Cerebral Ischemia by Promoting Proinflammatory Microglia Activation
Abstract
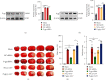
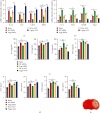
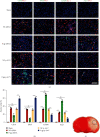
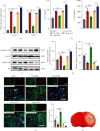
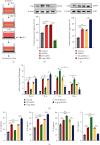
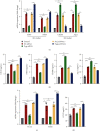
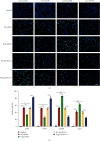
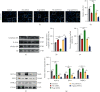
Microglia are activated following cerebral ischemic insult. P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is an efflux transporter on microvascular endothelial cells and upregulated after cerebral ischemia. This study evaluated the effects and possible mechanisms of P-gp on microglial polarization/activation in mice after ischemic stroke. P-gp-specific siRNA and adeno-associated virus (p-AAV) were used to silence and overexpress P-gp, respectively. Middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/R) and oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) were performed in mice and cerebral microvascular endothelial cells (bEnd.3) in vitro, respectively. OGD/R-injured bEnd.3 cells were cocultured with mouse microglial cells (BV2) in Transwell. Influences on acute ischemic stroke outcome, the expression of inflammatory cytokines, and chemokines and chemokines receptors, microglial polarization, glucocorticoid receptor (GR) nuclear translocation, and GR-mediated mRNA decay (GMD) activation were evaluated via reverse transcription real-time polymerase chain reaction, western blot, or immunofluorescence. Silencing P-gp markedly alleviated experimental ischemia injury as indicated by reduced cerebral infarct size, improved neurological deficits, and reduced the expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-12 expression. Silencing P-gp also mitigated proinflammatory microglial polarization and the expression of C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) and its receptor CCR2 expression, whereas promoted anti-inflammatory microglia polarization. Additionally, P-gp silencing promoted GR nuclear translocation and the expression of GMD relative proteins in endothelial cells. Conversely, overexpressing P-gp via p-AAV transfection offset all these effects. Furthermore, silencing endothelial GR counteracted all effects mediated by silencing or overexpressing P-gp. Elevated P-gp expression aggravated inflammatory response and brain damage after ischemic stroke by augmenting proinflammatory microglial polarization in association with increased endothelial CCL2 release due to GMD inhibition by P-gp.
Copyright © 2023 Yan Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No author has an actual or perceived conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Loureirin B protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through modulating M1/M2 microglial polarization via STAT6 / NF-kappaB signaling pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 15;953:175860. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175860. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37331681 Review.
-
Downregulation of Nogo-B ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice through regulating microglia polarization via TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway.Neurochem Int. 2023 Jul;167:105553. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2023.105553. Epub 2023 May 23. Neurochem Int. 2023. PMID: 37230196 Review.
-
Circular RNA PTP4A2 regulates microglial polarization through STAT3 to promote neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Apr;30(4):e14512. doi: 10.1111/cns.14512. Epub 2023 Oct 23. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 37869777 Free PMC article.
-
AEBP1 Silencing Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Regulating Neuron Ferroptosis and Microglia M2 Polarization Through PRKCA-PI3K-Akt Axis.Drug Dev Res. 2024 Dec;85(8):e70032. doi: 10.1002/ddr.70032. Drug Dev Res. 2024. PMID: 39670965
-
Shikonin attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting NOD2/RIP2/NF-κB-mediated microglia polarization and neuroinflammation.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024 Jun;33(6):107689. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2024.107689. Epub 2024 Mar 26. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 38527567
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

