Enabling genome editing in tropical maize lines through an improved, morphogenic regulator-assisted transformation protocol
- PMID: 38144709
- PMCID: PMC10748596
- DOI: 10.3389/fgeed.2023.1241035
Enabling genome editing in tropical maize lines through an improved, morphogenic regulator-assisted transformation protocol
Abstract
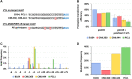
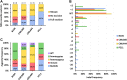
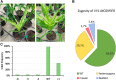
The recalcitrance exhibited by many maize (Zea mays) genotypes to traditional genetic transformation protocols poses a significant challenge to the large-scale application of genome editing (GE) in this major crop species. Although a few maize genotypes are widely used for genetic transformation, they prove unsuitable for agronomic tests in field trials or commercial applications. This challenge is exacerbated by the predominance of transformable maize lines adapted to temperate geographies, despite a considerable proportion of maize production occurring in the tropics. Ectopic expression of morphogenic regulators (MRs) stands out as a promising approach to overcome low efficiency and genotype dependency, aiming to achieve 'universal' transformation and GE capabilities in maize. Here, we report the successful GE of agronomically relevant tropical maize lines using a MR-based, Agrobacterium-mediated transformation protocol previously optimized for the B104 temperate inbred line. To this end, we used a CRISPR/Cas9-based construct aiming at the knockout of the VIRESCENT YELLOW-LIKE (VYL) gene, which results in an easily recognizable phenotype. Mutations at VYL were verified in protoplasts prepared from B104 and three tropical lines, regardless of the presence of a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) at the seed region of the VYL target site in two of the tropical lines. Three out of five tropical lines were amenable to transformation, with efficiencies reaching up to 6.63%. Remarkably, 97% of the recovered events presented indels at the target site, which were inherited by the next generation. We observed off-target activity of the CRISPR/Cas9-based construct towards the VYL paralog VYL-MODIFIER, which could be partly due to the expression of the WUSCHEL (WUS) MR. Our results demonstrate efficient GE of relevant tropical maize lines, expanding the current availability of GE-amenable genotypes of this major crop.
Keywords: Agrobacterium; B104; BABY BOOM; CRISPR/Cas9; VIRESCENT YELLOW-LIKE; WUSCHEL; off-target; protoplast.
Copyright © 2023 Hernandes-Lopes, Pinto, Vieira, Monteiro, Gerasimova, Nonato, Bruno, Vikhorev, Rausch-Fernandes, Gerhardt, Pauwels, Arruda, Dante and Yassitepe.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Adenle A. A., De Steur H., Hefferon K., Wesseler J. (2020). “Two decades of GMOs,” in Science, technology, and innovation for sustainable development Goals (United Kingdom: Oxford University Press; ), 401–422. 10.1093/oso/9780190949501.003.0020 - DOI
-
- Aesaert S., Impens L., Coussens G., Van Lerberge E., Vanderhaeghen R., Desmet L., et al. (2022). Optimized transformation and gene editing of the B104 public maize inbred by improved tissue culture and use of morphogenic regulators. Front. Plant Sci. 13 (April), 883847. 10.3389/fpls.2022.883847 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmad S., Shahzad R., Jamil S., Tabassum J., Chaudhary M. A. M., Atif R. M., et al. (2021a). “Regulatory aspects, risk assessment, and toxicity associated with RNAi and CRISPR methods. Cris. RNAi Syst. Nanobiotechnology Approaches to Plant Breed,” in Prot. A vol. Nanobiotechnology plant prot. (Berlin, Germany: Springer; ), 687–721. 10.1016/B978-0-12-821910-2.00013-8 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

