Effects of the active amyloid beta immunotherapy CAD106 on PET measurements of amyloid plaque deposition in cognitively unimpaired APOE ε4 homozygotes
- PMID: 38145469
- PMCID: PMC10984441
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.13532
Effects of the active amyloid beta immunotherapy CAD106 on PET measurements of amyloid plaque deposition in cognitively unimpaired APOE ε4 homozygotes
Abstract
Introduction: Alzheimer's Prevention Initiative Generation Study 1 evaluated amyloid beta (Aβ) active immunotherapy (vaccine) CAD106 and BACE-1 inhibitor umibecestat in cognitively unimpaired 60- to 75-year-old participants at genetic risk for Alzheimer's disease (AD). The study was reduced in size and terminated early. Results from the CAD106 cohort are presented.
Methods: Sixty-five apolipoprotein E ε4 homozygotes with/without amyloid deposition received intramuscular CAD106 450 μg (n = 42) or placebo (n = 23) at baseline; Weeks 1, 7, 13; and quarterly; 51 of them had follow-up Aβ positron emission tomography (PET) scans at 18 to 24 months.
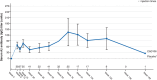
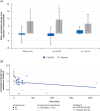
Results: CAD106 induced measurable serum Aβ immunoglobulin G titers in 41/42 participants, slower rates of Aβ plaque accumulation (mean [standard deviation] annualized change from baseline in amyloid PET Centiloid: -0.91[5.65] for CAD106 versus 8.36 [6.68] for placebo; P < 0.001), and three amyloid-related imaging abnormality cases (one symptomatic).
Discussion: Despite early termination, these findings support the potential value of conducting larger prevention trials of Aβ active immunotherapies in individuals at risk for AD.
Highlights: This was the first amyloid-lowering prevention trial in persons at genetic risk of late-onset Alzheimer's disease (AD). Active immunotherapy targeting amyloid (CAD106) was tested in this prevention trial. CAD106 significantly slowed down amyloid plaque deposition in apolipoprotein E homozygotes. CAD106 was generally safe and well tolerated, with only three amyloid-related imaging abnormality cases (one symptomatic). Such an approach deserves further evaluation in larger AD prevention trials.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; CAD106; active immunotherapy; amyloid; apolipoprotein E genotype; biomarkers; cognitively unimpaired; positron emission tomography; preclinical; prevention; vaccine.
© 2023 Novartis. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
M.E.R., Y.S., P.C., J.R., K.M., A.C. and A.G. are employees of and shareholders in Novartis. M.E.R. has a US patent application pending covering a pharmaceutical formulation containing CAD106 and an adjuvant and its use in Aβ immunotherapy. A.G. has a US patent covering CAD106 and its use in Ab immunotherapy. This research was sponsored by Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland. R.S.T. benefited from research support to Georgetown University from Lilly, Biogen, Roche, Genentech, Novartis, Janssen, and Eisai. J.O.R. serves as a neurology consultant for Clinical Research Services Turku (CRST Oy). P.N.T., E.M.R. and J.B.L. are full‐time employees of Banner Health. Banner Health received financial support from Novartis Pharma AG and Amgen for the conduct of the API Generation Program, from Eli Lilly for the conduct of another Alzheimer's prevention trial, and from Genentech/Roche for another Alzheimer's prevention trial. P.N.T. reports receiving grants from the National Institute on Aging (NIA) (UF1AG046150, RF1 AG041705, R01AG055444, and 1R01AG058468) and received consulting fees from AbbVie, AC Immune, Acadia, Axsome, Biogen, BioXcel, Cortexyme, Eisai, Genentech, Lundbeck, Otsuka & Astex, Merck & Co., Novo Nordisk, Syneos, and T3D Therapeutics. E.M.R. reports receiving grants from the NIA (1UF1AG046150, RF1AG041705, R01AG05544, 1R01AG058468, P30AG19610, and P30AG072980). He is a compensated scientific advisor for Alzheon, Aural Analytics, Denali, Retromer Therapeutics, and Vaxxinity and an uncompensated advisor to Biogen and Eli Lilly. He is the co‐founder, advisor, and shareholder in ALZPath. J.B.L. reports receiving grants from NIA (1UF1AG046150, RF1AG041705, R01AG05544, 1R01AG058468, and P30AG072980) and received consulting fees from Alector, Biogen, Denovo Biopharma, and Provoc. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain imaging measurements of fibrillar amyloid-β burden, paired helical filament tau burden, and atrophy in cognitively unimpaired persons with two, one, and no copies of the APOE ε4 allele.Alzheimers Dement. 2020 Apr;16(4):598-609. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2019.08.195. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Alzheimers Dement. 2020. PMID: 31831374 Free PMC article.
-
APOE ε4 gene dose effect on imaging and blood biomarkers of neuroinflammation and beta-amyloid in cognitively unimpaired elderly.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023 Apr 4;15(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13195-023-01209-6. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37016464 Free PMC article.
-
The Alzheimer's Prevention Initiative Generation Program: Study design of two randomized controlled trials for individuals at risk for clinical onset of Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2019 Jun 12;5:216-227. doi: 10.1016/j.trci.2019.02.005. eCollection 2019. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2019. PMID: 31211217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outreach, Screening, and Randomization of APOE ε4 Carriers into an Alzheimer's Prevention Trial: A global Perspective from the API Generation Program.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2023;10(3):453-463. doi: 10.14283/jpad.2023.27. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 37357285 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Understanding disease progression and improving Alzheimer's disease clinical trials: Recent highlights from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative.Alzheimers Dement. 2019 Jan;15(1):106-152. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Oct 13. Alzheimers Dement. 2019. PMID: 30321505 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Therapeutics for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Molecules. 2024 Oct 30;29(21):5131. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215131. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Active Immunization Targeting Amyloid β for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Neurodegener Dis. 2025 May 10:1-16. doi: 10.1159/000546287. Online ahead of print. Neurodegener Dis. 2025. PMID: 40349697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglial activation states and their implications for Alzheimer's Disease.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025 Jan;12(1):100013. doi: 10.1016/j.tjpad.2024.100013. Epub 2025 Jan 1. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025. PMID: 39800461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversibility of cognitive worsening observed with BACE inhibitor umibecestat in the Alzheimer's Prevention Initiative (API) Generation Studies.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Nov;20(11):7745-7761. doi: 10.1002/alz.14237. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 39320017 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Insights into the use of biomarkers in clinical trials in Alzheimer's disease.EBioMedicine. 2024 Oct;108:105322. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105322. Epub 2024 Oct 3. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39366844 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Dyck CH, Swanson CJ, Aisen P, et al. Lecanemab in early Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 2023;388:9‐21. - PubMed
-
- Zhu H, Mehta M, Huang SM, Wang Y. Toward bridging unmet medical need in early Alzheimer's disease: an evaluation of Beta‐Amyloid (Aβ) plaque burden as a potential drug development tool. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022;111:728‐731. - PubMed
-
- Chackerian B, Rangel M, Hunter Z, Peabody DS. Virus and virus‐like particle‐based immunogens for Alzheimer's disease induce antibody responses against amyloid‐beta without concomitant T cell responses. Vaccine. 2006;24:6321‐6331. - PubMed
-
- Winblad B, Andreasen N, Minthon L, et al. Safety, tolerability, and antibody response of active Aβ immunotherapy with CAD106 in patients with Alzheimer's disease: randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, first‐in‐human study. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11:597‐604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

