Regulatory mechanisms of autophagy-related ncRNAs in bone metabolic diseases
- PMID: 38146458
- PMCID: PMC10749346
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1178310
Regulatory mechanisms of autophagy-related ncRNAs in bone metabolic diseases
Abstract
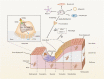
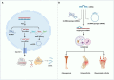
Bone metabolic diseases have been tormented and are plaguing people worldwide due to the lack of effective and thorough medical interventions and the poor understanding of their pathogenesis. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are heterogeneous transcripts that cannot encode the proteins but can affect the expressions of other genes. Autophagy is a fundamental mechanism for keeping cell viability, recycling cellular contents through the lysosomal pathway, and maintaining the homeostasis of the intracellular environment. There is growing evidence that ncRNAs, autophagy, and crosstalk between ncRNAs and autophagy play complex roles in progression of metabolic bone disease. This review investigated the complex mechanisms by which ncRNAs, mainly micro RNAs (miRNAs), long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs), regulate autophagic pathway to assist in treating bone metabolism disorders. It aimed at identifying the autophagy role in bone metabolism disorders and understanding the role, potential, and challenges of crosstalk between ncRNAs and autophagy for bone metabolism disorders treatment.
Keywords: autophagy; bone metabolism; ncRNAs; osteoarthritis; osteoporosis; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2023 Yan, Li, Su, Xue, Qiu, Xu and Tan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

