Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Neuraminidase Inhibition Antibodies in Healthy Adults after Exposure to Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09
- PMID: 38147510
- PMCID: PMC10756388
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3001.230756
Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Neuraminidase Inhibition Antibodies in Healthy Adults after Exposure to Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09
Abstract
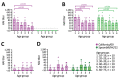
We detected high titers of cross-reactive neuraminidase inhibition antibodies to influenza A(H5N1) virus clade 2.3.4.4b in 96.8% (61/63) of serum samples from healthy adults in Hong Kong in 2020. In contrast, antibodies at low titers were detected in 42% (21/50) of serum samples collected in 2009. Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and A(H5N1) titers were correlated.
Keywords: clade 2.3.4.4.b; cross-reactive antibody response; influenza; influenza A(H1N1)pdm09; influenza A(H5N1); neuraminidase inhibition antibody; pandemic risk assessment; respiratory infections; viruses.
Figures
References
-
- Adlhoch C, Fusaro A, Gonzales JL, Kuiken T, Mirinaviciute G, Niqueux É, et al.; European Food Safety Authority, European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, European Union Reference Laboratory for Avian Influenza. Avian influenza overview March - April 2023. EFSA J. 2023;21:e08039. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Antigenic and genetic characteristics of zoonotic influenza A viruses and development of candidate vaccine viruses for pandemic preparedness. 2022. [cited 2023 May 18]. https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/influenza/who-influenza-re...
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

