Identification of highly selective SIK1/2 inhibitors that modulate innate immune activation and suppress intestinal inflammation
- PMID: 38147543
- PMCID: PMC10769863
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2307086120
Identification of highly selective SIK1/2 inhibitors that modulate innate immune activation and suppress intestinal inflammation
Abstract
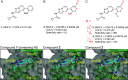
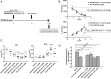
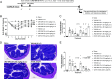
The salt-inducible kinases (SIK) 1-3 are key regulators of pro- versus anti-inflammatory cytokine responses during innate immune activation. The lack of highly SIK-family or SIK isoform-selective inhibitors suitable for repeat, oral dosing has limited the study of the optimal SIK isoform selectivity profile for suppressing inflammation in vivo. To overcome this challenge, we devised a structure-based design strategy for developing potent SIK inhibitors that are highly selective against other kinases by engaging two differentiating features of the SIK catalytic site. This effort resulted in SIK1/2-selective probes that inhibit key intracellular proximal signaling events including reducing phosphorylation of the SIK substrate cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) regulated transcription coactivator 3 (CRTC3) as detected with an internally generated phospho-Ser329-CRTC3-specific antibody. These inhibitors also suppress production of pro-inflammatory cytokines while inducing anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 in activated human and murine myeloid cells and in mice following a lipopolysaccharide challenge. Oral dosing of these compounds ameliorates disease in a murine colitis model. These findings define an approach to generate highly selective SIK1/2 inhibitors and establish that targeting these isoforms may be a useful strategy to suppress pathological inflammation.
Keywords: immunological disorders; inflammatory bowel disease; kinase inhibitors; medicinal chemistry; structure-based drug design.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors’ employment information at the time of data generation are marked in the “Author affiliations” section. H.B., T.B.S., M.T., M.S., G.B., W.C., L.C, De M.C., K.C., B.C., M.F., A.G., P.A.M., A.M., E.V.M.-M., M.-L.R., M.R., P.L.S., R. Smith, J. Smith, R. Steele, H.S., J. Suarez, G.T., N.M., L.P.V., J.W., P.T.D., L.L.O., T.K., S.D.G., G.H., T.O., N.S., S.P., J.D.V., J.E.T. are current or former employees of Janssen Research & Development, LLC, and employees may own stock/stock options in Johnson & Johnson, of which Janssen Research & Development, LLC is a subsidiary. R.J.X. is co-founder of Jnana Therapeutics and Celsius Therapeutics, scientific advisory board member at Nestlé and Magnet BioMedicine, board director at MoonLake Immunotherapeutics; these organizations had no roles in this study. G.B., W.C., De M.C., S.D.G., G.H., V.K.K., E.V.M.-M., D.D.R., H.S., M.S., R. Smith, T.B.S., M.T., J.D.V., J.W., and R.J.X. are named as inventors on the PCT patent application “Small Molecule Inhibitors of Salt Inducible Kinases”, published as WO 2022/165529, and N.M., R.J.X., T.B.S., G.T., and H.B. are named inventors on the PCT patent application “Materials and Methods for Differentiating CREB Regulated Transcription Coactivator 3”, published as WO 2022/260995.
Figures

References
-
- Lombardi M. S., Gillieron C., Dietrich D., Gabay C., SIK inhibition in human myeloid cells modulates TLR and IL-1R signaling and induces an anti-inflammatory phenotype. J. Leukocyte Biol. 99, 711–721 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

