ANGPTL4 binds to the leptin receptor to regulate ectopic bone formation
- PMID: 38147550
- PMCID: PMC10769826
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2310685120
ANGPTL4 binds to the leptin receptor to regulate ectopic bone formation
Abstract
Leptin protein was thought to be unique to leptin receptor (LepR), but the phenotypes of mice with mutation in LepR [db/db (diabetes)] and leptin [ob/ob (obese)] are not identical, and the cause remains unclear. Here, we show that db/db, but not ob/ob, mice had defect in tenotomy-induced heterotopic ossification (HO), implicating alternative ligand(s) for LepR might be involved. Ligand screening revealed that ANGPTL4 (angiopoietin-like protein 4), a stress and fasting-induced factor, was elicited from brown adipose tissue after tenotomy, bound to LepR on PRRX1+ mesenchymal cells at the HO site, thus promotes chondrogenesis and HO development. Disruption of LepR in PRRX1+ cells, or lineage ablation of LepR+ cells, or deletion of ANGPTL4 impeded chondrogenesis and HO in mice. Together, these findings identify ANGPTL4 as a ligand for LepR to regulate the formation of acquired HO.
Keywords: ANGPTL4; heterotopic ossification; leptin receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
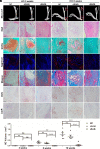



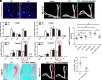
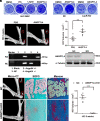

References
-
- Zhang Y., et al. , Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 372, 425–432 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Friedman J. M., Halaas J. L., Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 395, 763–770 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Lee G. H., et al. , Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Nature 379, 632–635 (1996). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82301002/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 92268204/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 81991511/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 2019A1515110148/GDSTC | Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province ()
- 2022M711510/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (China Postdoctoral Foundation Project)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

