Molecular chaos under the skin: Epigenetic reprogramming in hidradenitis suppurativa
- PMID: 38147564
- PMCID: PMC10769847
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2319797121
Molecular chaos under the skin: Epigenetic reprogramming in hidradenitis suppurativa
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
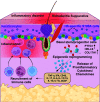
Comment on
-
Epigenetic switch reshapes epithelial progenitor cell signatures and drives inflammatory pathogenesis in hidradenitis suppurativa.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Dec 5;120(49):e2315096120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2315096120. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 38011564 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Increased epigenetic age acceleration in the hidradenitis suppurativa skin.Arch Dermatol Res. 2023 May;315(4):1037-1039. doi: 10.1007/s00403-022-02432-1. Epub 2022 Oct 29. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023. PMID: 36308559
-
A gene dysfunction module reveals the underlying pathogenesis of hidradenitis suppurativa: An update.Australas J Dermatol. 2020 Feb;61(1):e10-e14. doi: 10.1111/ajd.13107. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Australas J Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31266094 Review.
-
Reduced ten-eleven translocation and isocitrate dehydrogenase expression in inflammatory hidradenitis suppurativa lesions.Eur J Dermatol. 2018 Aug 1;28(4):449-456. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2018.3369. Eur J Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 30325321
-
Altered Global 5-Hydroxymethylation Status in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Support for an Epigenetic Background.Dermatology. 2017;233(2-3):129-135. doi: 10.1159/000478043. Epub 2017 Jul 28. Dermatology. 2017. PMID: 28750404
-
Registries, multicentre and genome-wide association studies in hidradenitis suppurativa.Exp Dermatol. 2022 Sep;31 Suppl 1:22-28. doi: 10.1111/exd.14610. Exp Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35582836 Review.
References
-
- Goldburg S. R., Strober B. E., Payette M. J., Hidradenitis suppurativa: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, and pathogenesis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 82, 1045–1058 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Goldburg S. R., Strober B. E., Payette M. J., Hidradenitis suppurativa: Current and emerging treatments. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 82, 1061–1082 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

