Single-shot diffusion trace-weighted MR spectroscopy: Comparison with unipolar and bipolar diffusion-weighted point-resolved spectroscopy
- PMID: 38148181
- PMCID: PMC10957108
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.5090
Single-shot diffusion trace-weighted MR spectroscopy: Comparison with unipolar and bipolar diffusion-weighted point-resolved spectroscopy
Abstract
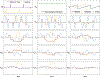
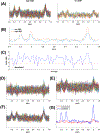
This study demonstrates the feasibility and performance of the point-resolved spectroscopy (PRESS)-based, single-shot diffusion trace-weighted sequence in quantifying the trace apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) in phantom and in vivo using a 3-T MRI/MRS scanner. The single-shot diffusion trace-weighted PRESS sequence was implemented and compared with conventional diffusion-weighted (DW)-PRESS variants using bipolar and unipolar diffusion-sensitizing gradients. Nine phantom datasets were acquired using each sequence, and seven volunteers were scanned in three different brain regions to determine the range and variability of trace ADC values, and to allow a comparison of trace ADCs among the sequences. This sequence results in a comparatively stable range of trace ADC values that are statistically significantly higher than those produced from unipolar and bipolar DW-PRESS sequences. Only total n-acetylaspartate, total creatine, and total choline were reliably estimated in all sequences with Cramér-Rao lower bounds of, at most, 20%. The larger trace ADCs from the single-shot sequences are probably attributable to the shorter diffusion time relative to the other sequences. Overall, this study presents the first demonstration of the single-shot diffusion trace-weighted sequence in a clinical scanner at 3 T. The results show excellent agreement of phantom trace ADCs computed with all sequences, and in vivo ADCs agree well with the expected differences between gray and white matter. The diffusion trace-weighted sequence could provide an estimate of the trace ADC in a shorter scan time (by nearly a factor of 3) compared with conventional DW-PRESS approaches that require three separate orthogonal directions.
Keywords: b-value; diffusion tensor; diffusion-weighting; point-resolved spectroscopy; trace apparent diffusion coefficient.
© 2023 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





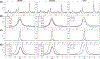
Similar articles
-
Single-shot diffusion trace spectroscopic imaging using radial echo planar trajectories.Magn Reson Med. 2024 Sep;92(3):926-944. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30125. Epub 2024 May 10. Magn Reson Med. 2024. PMID: 38725389 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative evaluation of benign and malignant vertebral fractures with diffusion-weighted MRI: what is the optimum combination of b values for ADC-based lesion differentiation with the single-shot turbo spin-echo sequence?AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014 Sep;203(3):582-8. doi: 10.2214/AJR.13.11632. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014. PMID: 25148160
-
Distortion-free diffusion MRI using an MRI-guided Tri-Cobalt 60 radiotherapy system: Sequence verification and preliminary clinical experience.Med Phys. 2017 Oct;44(10):5357-5366. doi: 10.1002/mp.12465. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28692129
-
Multishot diffusion-prepared magnitude-stabilized balanced steady-state free precession sequence for distortion-free diffusion imaging.Magn Reson Med. 2019 Apr;81(4):2374-2384. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27565. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Magn Reson Med. 2019. PMID: 30488979
-
Diffusion-weighted MR of the brain: methodology and clinical application.Radiol Med. 2005 Mar;109(3):155-97. Radiol Med. 2005. PMID: 15775887 Review. English, Italian.
Cited by
-
High-resolution, volumetric diffusion-weighted MR spectroscopic imaging of the brain.Magn Reson Med. 2025 Aug;94(2):450-469. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30479. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 40065541 Free PMC article.

