In search of a pan-coronavirus vaccine: next-generation vaccine design and immune mechanisms
- PMID: 38148330
- PMCID: PMC10805787
- DOI: 10.1038/s41423-023-01116-8
In search of a pan-coronavirus vaccine: next-generation vaccine design and immune mechanisms
Abstract
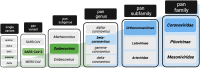
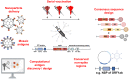
Members of the coronaviridae family are endemic to human populations and have caused several epidemics and pandemics in recent history. In this review, we will discuss the feasibility of and progress toward the ultimate goal of creating a pan-coronavirus vaccine that can protect against infection and disease by all members of the coronavirus family. We will detail the unmet clinical need associated with the continued transmission of SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV and the four seasonal coronaviruses (HCoV-OC43, NL63, HKU1 and 229E) in humans and the potential for future zoonotic coronaviruses. We will highlight how first-generation SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and natural history studies have greatly increased our understanding of effective antiviral immunity to coronaviruses and have informed next-generation vaccine design. We will then consider the ideal properties of a pan-coronavirus vaccine and propose a blueprint for the type of immunity that may offer cross-protection. Finally, we will describe a subset of the diverse technologies and novel approaches being pursued with the goal of developing broadly or universally protective vaccines for coronaviruses.
Keywords: Coronavirus; Cross-protection; Cross-reactive immunity; Universal; Vaccine.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation, WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. 2023. https://covid19.who.int. Accessed 27 Oct 2023.
-
- Yang Z-R, Jiang YW, Li FX, Liu D, Lin TF, Zhao ZY, et al. Efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and the dose-response relationship with three major antibodies: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Microbe. 2023;4:e236–46. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(22)00390-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

