Meta-analysis of a mindfulness yoga exercise intervention on depression - based on intervention studies in China
- PMID: 38148781
- PMCID: PMC10750402
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1283172
Meta-analysis of a mindfulness yoga exercise intervention on depression - based on intervention studies in China
Abstract
Background: Using statistical methods to analyze and summarize the research data of the inclusion criteria, to provide a quantitative average effect size to interpret the influence of mindfulness yoga exercise on patients with different depressive symptoms, explain the therapeutic effect of mindfulness yoga therapy on depression and its possible mechanism of action, and provide new ideas for the clinical treatment of patients with depression.
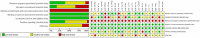
Method: Review Manage 5.4 software was used to comprehensively evaluate the effect of yoga exercise on depression interventions to provide a reference for improving mental health. CNKI, PubMed, Web of science, EBSCO were searched for all case-control research articles on yoga for depression from 2000 to 2022. After screening, data extraction and quality evaluation of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) by inclusion and exclusion criteria, a total of 22 studies with 2,216 patients were included, including 1,101 in the yoga intervention group and 1,115 in the control group.
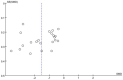
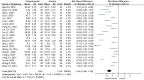
Results: The results showed a large heterogeneity in the literature on the effect of yoga exercise on depression, with a combined total effect size [SMD = -1.53, 95%CI (-1.96, -1.10), p < 0.00001].
Conclusion: Mindfulness yoga exercise is effective in preventing and treating depression and improving mental health, and may be considered as a non-medical, low-cost intervention as an adjunct to pharmacological treatment.
Keywords: anxiety; depression; meta-analysis; mindfulness thinking; yoga exercises.
Copyright © 2023 Yang, Cao, Lyu and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Amitani M., Amitani H., Owaki T., Monuki T., Adachi S., Kawazu S., et al. . (2022). The effect of mindfulness yoga in children with school refusal: a study protocol for an exploratory, cluster-randomized, open, standard care-controlled, Multicenter clinical trial. Front. Public Health 10:881303. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.881303, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bao W. L., Qiu L. W., Wu J., Feng W. (2015). Intervention effect of yoga exercise on university students with depression. J. Kunming Med. Univ. 36, 169–180.
-
- Chen Y. C., Ye E. M. (2020). Application of mindfulness meditation training combined with group yoga intervention in patients with manic depression. Nurs. Integr. Tradit. Chinese Western Med. 6, 134–141.
-
- China Education and Research Network (2022). 2022 National Depression Blue Book. Available at: http://xlfd.hsu.edu.cn/7e/0f/c33a163343/page.htm.
-
- Daley A. J., Foster L., Long G., Palmer C., Robinson O., Walmsley H., et al. . (2015). The effectiveness of exercise for the prevention and treatment of antenatal depression: systematic review with meta-analysis. BJOG 122:1. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources