A novel conceptual model of heart rate autonomic modulation based on a small-world modular structure of the sinoatrial node
- PMID: 38148905
- PMCID: PMC10750401
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1276023
A novel conceptual model of heart rate autonomic modulation based on a small-world modular structure of the sinoatrial node
Abstract
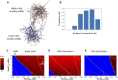
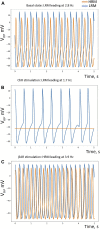
The present view on heartbeat initiation is that a primary pacemaker cell or a group of cells in the sinoatrial node (SAN) center paces the rest of the SAN and the atria. However, recent high-resolution imaging studies show a more complex paradigm of SAN function that emerges from heterogeneous signaling, mimicking brain cytoarchitecture and function. Here, we developed and tested a new conceptual numerical model of SAN organized similarly to brain networks featuring a modular structure with small-world topology. In our model, a lower rate module leads action potential (AP) firing in the basal state and during parasympathetic stimulation, whereas a higher rate module leads during β-adrenergic stimulation. Such a system reproduces the respective shift of the leading pacemaker site observed experimentally and a wide range of rate modulation and robust function while conserving energy. Since experimental studies found functional modules at different scales, from a few cells up to the highest scale of the superior and inferior SAN, the SAN appears to feature hierarchical modularity, i.e., within each module, there is a set of sub-modules, like in the brain, exhibiting greater robustness, adaptivity, and evolvability of network function. In this perspective, our model offers a new mainframe for interpreting new data on heterogeneous signaling in the SAN at different scales, providing new insights into cardiac pacemaker function and SAN-related cardiac arrhythmias in aging and disease.
Keywords: autonomic modulation of heart rate; cell heterogeneity; heartbeat; numerical model; pacemaker mechanism; shift of the leading pacemaker site; sinoatrial node; small-world network.
Copyright © 2023 Maltsev, Stern, Lakatta and Maltsev.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Aldous D. (1989). Probability approximations via the Poisson clumping heuristic. Applied mathematical sciences 7. New York, NY: Springer.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

