A predictive model for residual lesions after LEEP surgery in CIN III patients
- PMID: 38148909
- PMCID: PMC10751019
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1326833
A predictive model for residual lesions after LEEP surgery in CIN III patients
Abstract
Background and aims: The residual lesions after Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure (LEEP) contributes to poor prognosis in patients with Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Grade 3 (CIN3). The aim of this study is to establish an effective clinical predictive model for residual lesions in CIN3 patients after LEEP.
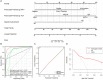
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed on 436 CIN3 patients who underwent total hysterectomy within 3 months after LEEP. Based on the post-hysterectomy pathologic, the patients were divided into the no residual group and residual group. Clinical parameters were compared between the two groups, and univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were conducted to identify independent risk factors for residual lesions in CIN3 patients after LEEP. Using R software, a nomogram model was established and its effectiveness was evaluated using calibration plots.
Results: There were 178 cases in the residual group and 258 cases in the no residual group. The two groups had no significant difference in general characteristics (p > 0.05). It was found that Post-LEEP follow-up HPV, Post-LEEP follow-up TCT, and the Gland involvement were independent risk factors for residual lesions in CIN3 patients after LEEP (all p < 0.05). The consistency index (C-index) of the nomogram model for predicting residual lesions was 0.975 (0.962-0.988).
Conclusion: The Post-LEEP follow-up HPV, Post-LEEP follow-up TCT, and Gland involvement are independent risk factors related to residual tissue after LEEP surgery in CIN3 patients. The constructed nomogram can effectively predict the presence of residual tissue after LEEP surgery in CIN3 patients and has good practical value.
Keywords: LEEP; cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade III; nomogram LEEP; post-total hysterectomy; predictive model.
Copyright © 2023 Deng, Wang, Chen, Tang and Xiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kyrgiou M, Athanasiou A, Arbyn M, Lax SF, Raspollini MR, Nieminen P, et al. Terminology for cone dimensions after local conservative treatment for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and early invasive cervical cancer: 2022 consensus recommendations from ESGO, EFC, IFCPC, and ESP. Lancet Oncol. (2022) 23:e385–92. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00191-7 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

