Ultrasound characterization of superficial lymph nodes in HIV patients with Talaromyces marneffei infection
- PMID: 38148912
- PMCID: PMC10750475
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1243599
Ultrasound characterization of superficial lymph nodes in HIV patients with Talaromyces marneffei infection
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed at exploring the ultrasound characteristics of superficial lymph nodes (LNs) in HIV patients with Talaromyces marneffei infection to provide assistance and understanding for diagnosis and therapy.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 26 patients with confirmed HIV and T.marneffei coinfection. These patients underwent ultrasound examination and ultrasound-guided puncture biopsies at our hospital from March 2015 to March 2023.
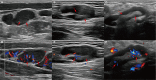
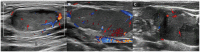
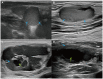
Results: In all 26 patients, lymphadenectasis was observed. Among the 21 cases (80.76%), LNs showed a diffusely hyperechoic appearance with a tulle-like change, and 6 cases (23.07%) showed liquefaction. When the hila were present or thinned, the blood flow signals were primarily hilar, whether rich or poor, and when the hila were absent, the blood flow signals were peripheral or poor. The axillary LN long-to-short diameter (L/S) ratios exhibited a significant positive correlation with CD4+T cell counts (r = 0.8214, p = 0.0341). Patients with retroperitoneal lymphadenectasis showed decreased NK cell counts (p = 0.03).
Conclusion: In summary, the T.marneffei infection of LNs in HIV patients often manifests with superficial LN enlargement, mostly affecting the cervical LNs. The T.marneffei-infected LNs exhibit several characteristics such as echogenicity, hilum, and blood flow signal. Furthermore, there might be associations between lymphocyte subsets and enlarged superficial LNs. Ultrasound examinations should be paid attention to if patients have superficial LN enlargement, and the diagnosis of the T.marneffei infection is considered.
Keywords: HIV; Talaromyces marneffei; diagnosis; lymph node; ultrasound.
Copyright © 2023 Pan and Shao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Coinfection of disseminated Talaromyces marneffei and Mycobacteria kansasii in a patient with papillary thyroid cancer: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Dec;96(52):e9072. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009072. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29384899 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral immune profile of children with Talaromyces marneffei infections: a retrospective analysis of 21 cases.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Mar 20;21(1):287. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-05978-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33743629 Free PMC article.
-
CT findings of Talaromyces marneffei infection among HIV patients with lymphadenopathy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 27;9:930678. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.930678. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36250101 Free PMC article.
-
Talaromyces Marneffei Infection in an HIV-Negative Child with a CARD9 Mutation in China: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Mycopathologia. 2021 Aug;186(4):553-561. doi: 10.1007/s11046-021-00576-8. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Mycopathologia. 2021. PMID: 34224076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics and Prognosis of Talaromyces marneffei Infection in HIV-positive Children in Southern China.Mycopathologia. 2022 Jun;187(2-3):169-180. doi: 10.1007/s11046-021-00614-5. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Mycopathologia. 2022. PMID: 35157189 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

