Development and validation of a novel nomogram model for predicting the survival of patients with T2-4a, N0-x, M0 bladder cancer: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 38148935
- PMCID: PMC10749381
Development and validation of a novel nomogram model for predicting the survival of patients with T2-4a, N0-x, M0 bladder cancer: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Objective: Recent developments in bladder cancer treatment strategies have significantly improved the prognosis of clinically curable muscle invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) patients. Here, the prognostic factors of T2-4a, N0-x, M0 MIBC patients were investigated using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database and a novel nomogram model was established for prognosis prediction.
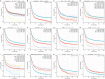
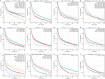
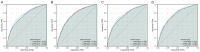
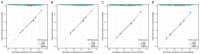
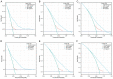
Methods: The data of 7,292 patients with T2-4a, N0-x, M0 MIBC were retrieved from the SEER database (2000-2020) and randomly classified into a training set (n = 5,106) and validation set (n = 2,188). Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to calculate cancer-specific survival (CSS) and overall survival (OS) rates of patients, and differences between survival curves were analyzed using the log-rank test. Cox regression analysis was used to screen and incorporate patient prognosis-affecting independent risk factors into the nomogram model. Consistency index (C-index) values and areas under the time-dependent receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) were used to evaluate the discriminatory ability, and the calibration curve was used to assess the calibration of the model. Its predictive performance and American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage were compared using decision curve analysis (DCA).
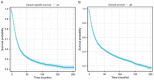
Results: The 1-, 3-, and 5-year CSS and OS rates of patients with T2-4a, N0-x, M0 MIBC were 76.9%, 56.0%, and 49.9%, respectively, and 71.3%, 47.9%, and 39.5%, respectively. Cox regression analysis showed that age, marital status, race, pathological type, tumor size, AJCC stage, T stage, N stage, surgery of primary tumor, regional lymph node dissection, radiation, and chemotherapy were independent prognostic risk factors of both CSS and OS (P < 0.05). The C-index and AUC of the nomogram model constructed based on the training and validation sets were both > 0.7, and calibration curves for predicting the 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival were consistent with the ideal curve. The nomogram model showed a higher net benefit with DCA than AJCC stage analysis.
Conclusion: The nomogram model could accurately predict the prognosis of patients with T2-4a, N0-x, M0 MIBC. It may help clinicians perform personalized prognosis evaluations and formulate treatment plans.
Keywords: Muscle invasive bladder cancer; SEER database; nomogram model; survival prognosis.
AJCEU Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and validation of a nomogram model for cancer-specific survival of patients with poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma: A SEER database analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 13;13:882279. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.882279. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36176465 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Predictive Value of the Log Odds of Negative Lymph Nodes/T Stage as a Novel Prognostic Factor in Bladder Cancer Patients After Radical Cystectomy.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 19;12:895413. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.895413. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35928878 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic nomogram for primary splenic lymphoma: a SEER database-based study.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 15;13(12):5825-5845. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38187057 Free PMC article.
-
Nomograms-based prediction of overall and cancer-specific survivals for patients diagnosed with major salivary gland carcinoma.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Aug;9(15):1230. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-1725. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34532367 Free PMC article.
-
A postsurgical prognostic nomogram for patients with lymph node positive rectosigmoid junction adenocarcinoma.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 May 18;23(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02810-7. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37202718 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Milowsky MI, Rumble RB, Booth CM, Gilligan T, Eapen LJ, Hauke RJ, Boumansour P, Lee CT. Guideline on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer (European Association of Urology Guideline): American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline endorsement. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016;34:1945–1952. - PubMed
-
- Witjes JA, Bruins HM, Cathomas R, Comperat EM, Cowan NC, Gakis G, Hernandez V, Linares Espinos E, Lorch A, Neuzillet Y, Rouanne M, Thalmann GN, Veskimae E, Ribal MJ, van der Heijden AG. European Association of Urology Guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: summary of the 2020 guidelines. Eur Urol. 2021;79:82–104. - PubMed
-
- EAU Guidelines. Arnhem, The Netherlands: EAU Guidelines Office; 2023.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
