Macropinocytosis as a potential mechanism driving neurotropism of Cryptococcus neoformans
- PMID: 38149006
- PMCID: PMC10750359
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1331429
Macropinocytosis as a potential mechanism driving neurotropism of Cryptococcus neoformans
Abstract
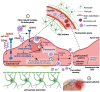
Cryptococcus neoformans can invade the central nervous system by crossing the blood-brain barrier via a transcellular mechanism that relies on multiple host factors. In this narrative, we review the evidence that a direct interplay between C. neoformans and brain endothelial cells forms the basis for invasion and transmigration across the brain endothelium. Adherence and internalization of C. neoformans is dependent on transmembrane proteins, including a hyaluronic acid receptor and an ephrin receptor tyrosine kinase. We consider the role of EphA2 in facilitating the invasion of the central nervous system by C. neoformans and highlight experimental evidence supporting macropinocytosis as a potential mechanism of internalization and transcytosis. How macropinocytosis might be conclusively demonstrated in the context of C. neoformans is also discussed.
Keywords: CD44; EphA2; Ephrin receptor; EphrinA1; blood-brain barrier; brain endothelial cells; macropinocytosis; transcytosis.
Copyright © 2023 Lanser, Bennett, Vu and Gelli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Bandyopadhyay C., Valiya-Veettil M., Dutta D., Chakraborty S., Chandran B. (2014). CIB1 synergizes with EphrinA2 to regulate Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus macropinocytic entry in human microvascular dermal endothelial cells. PloS Pathog. 10 (2), e1003941. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003941 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

