Esophageal Stent Migration Diagnosed With Point-of-Care Ultrasound
- PMID: 38149125
- PMCID: PMC10750131
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.49418
Esophageal Stent Migration Diagnosed With Point-of-Care Ultrasound
Abstract
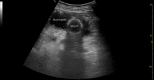
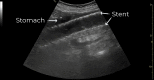
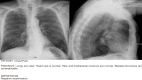
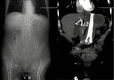
This unique case depicts the first published report of a physician using point-of-care ultrasound to diagnose an esophageal stent migration. Discussed in this article are the sonographic findings that clinicians should be familiar with when evaluating patients with abdominal pain or chest pain who have a history of an esophageal stent. When coupled with a high index of suspicion, ultrasound can be one of the most portable, readily available, low-cost, and minimally invasive techniques for making a rapid diagnosis of esophageal stent migration.
Keywords: abdominal imaging; abdominal pain; chest pain; emergency medicine physician; esophageal stent; esophageal stent migration; point-of-care ultrasound; sonography; stomach; ultrasound.
Copyright © 2023, Harris et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
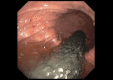
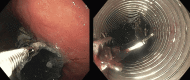
References
-
- Esophageal stent migration can lead to intestinal obstruction. Karatepe O, Acet E, Altiok M, Battal M, Adas G, Karahan S. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3364652/ N Am J Med Sci. 2009;1:63–65. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) and its potential to advance patient care in low-resource settings and conflict zones. Dana E, Nour AD, Kpa'Hanba GA, Khan JS. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2023;17:0. - PubMed
-
- Distally migrated esophageal self-expanding metal stents: wait and see or remove? De Palma GD, Lovino P, Catanzano C. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;53:96–98. - PubMed
-
- Migrated esophageal stent endoscopic extraction through gastrostomy site in a patient with severe esophageal stricture. Shin CM, Clayton SB. J Clin Gastroenterol Treat. 2019;5:64.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
