Immunomodulatory role of vasoactive intestinal peptide and ghrelin in Oncorhynchus mykiss
- PMID: 38149209
- PMCID: PMC10750074
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23215
Immunomodulatory role of vasoactive intestinal peptide and ghrelin in Oncorhynchus mykiss
Abstract
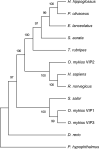
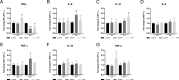
Neuropeptides are a group of peptides derived from precursor proteins synthesized in neuronal and nonneuronal cells. The classical functions of neuropeptides have been extensively studied in mammals, including neuromodulation in the central nervous system, molecular signaling in the peripheral nervous system, and immunomodulation associated mainly with anti-inflammatory activity. In contrast, in teleosts, studies of the immunomodulatory function of these neuropeptides are limited. In Oncorhynchus mykiss, vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) mRNA sequences have not been cloned, and the role of VIP in modulating the immune system has not been studied. Furthermore, in relation to other neuropeptides with possible immunomodulatory function, such as ghrelin, there are also few studies. Therefore, in this work, we performed molecular cloning, identification, and phylogenetic analysis of three VIP precursor sequences (prepro-VIP1, VIP2 and VIP3) in rainbow trout. In addition, the immunomodulatory function of both neuropeptides was evaluated in an in vitro model using the VIP1 sequence identified in this work and a ghrelin sequence already studied in O. mykiss. The results suggest that the prepro-VIP2 sequence has the lowest percentage of identity with respect to the other homologous sequences and is more closely related to mammalian orthologous sequences. VIP1 induces significant expression of both pro-inflammatory (IFN-γ, IL-1β) and anti-inflammatory (IL-10 and TGF-β) cytokines, whereas ghrelin only induces significant expression of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α.
Keywords: Cytokines; Ghrelin; Immune system; Neuropeptide; Oncorhynchus mykiss; RTS11 cell line; Vasoactive intestinal peptide.
© 2023 Universidad de Concepcion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
VIP1 and VIP2 receptors but not PVR1 mediate the effect of VIP/PACAP on cytokine production in T lymphocytes.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Dec 11;865:397-407. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb11204.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 9928038
-
Analogues of VIP, helodermin, and PACAP discriminate between rat and human VIP1 and VIP2 receptors.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Dec 11;865:247-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb11184.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 9928018
-
Regulatory effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide on cytokine production in central and peripheral lymphoid organs.Adv Neuroimmunol. 1996;6(1):61-74. doi: 10.1016/s0960-5428(96)00007-1. Adv Neuroimmunol. 1996. PMID: 8790782 Review.
-
Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide- and pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide-mediated control of catecholamine release from chromaffin tissue in the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss.J Endocrinol. 2000 Sep;166(3):705-14. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1660705. J Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10974664
-
Vasoactive intestinal peptide in thymus: synthesis, receptors and biological actions.Neuroimmunomodulation. 1999 Jan-Apr;6(1-2):97-107. doi: 10.1159/000026369. Neuroimmunomodulation. 1999. PMID: 9876240 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

