From game engagement to craving responses - The role of gratification and compensation experiences during video-gaming in casual and at-risk gamers
- PMID: 38149224
- PMCID: PMC10749870
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abrep.2023.100520
From game engagement to craving responses - The role of gratification and compensation experiences during video-gaming in casual and at-risk gamers
Abstract
Introduction: Although playing videogames is a common leisure activity some individuals develop problematic gaming behaviors or even symptoms of a gaming disorder. Game engagement may be involved in reinforcement learning that may result in experiences of craving, an important feature of gaming disorder. In the following study we aimed to approach the question which aspects contribute to increased craving for gaming.
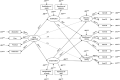
Methods: Overall, 439 individuals participated in an online survey, answering questionnaires on game engagement, experience of gratification and compensation, craving, and symptoms of gaming disorder. A mediation model testing if the association between game engagement and facets of craving are mediated by the experience of gratification and compensation during gaming.
Results: Three facets of craving (reward/relief, physiological, obsessive craving) were statistically explained by game engagement and the experience of gratification and compensation. Models differed between casual gamers and at-risk gamers. The effects on reward/relief and physiological craving were fully mediated in the casual group and partially mediated in the at-risk group by gratification and compensation experiences.
Conclusion: Game engagement may contribute to the development of craving by increasing the experience of gratification and compensation and thus might be important in reinforcement learning. Games evoking a high engagement may therefore have a higher addictive potential. Further processes potentially related to game engagement, such as intrusive thoughts and desire thinking, which are related to craving experiences, should be considered in future studies.
Keywords: Craving; Cue-reactivity; Engagement; Flow; Gaming; Immersion.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- American-Psychiatric-Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®). - PubMed
-
- Andrade J., May J., Kavanagh D.J. Sensory imagery in craving: From cognitive psychology to new treatments for addiction. Journal of Experimental Psychopathology. 2012;3(2):127–145. doi: 10.5127/jep.024611. - DOI
-
- Antons S., Müller S.M., Liebherr M., Brand M. Gaming disorder: How to translate behavioral neuroscience into public health advances. Current Behavioral Neuroscience Reports. 2020;7(4):267–277. doi: 10.1007/s40473-020-00216-3. - DOI
-
- Antons S., Trotzke P., Wegmann E., Brand M. Interaction of craving and functional coping styles in heterosexual males with varying degrees of unregulated Internet-pornography use. Personality and Individual Differences. 2019;149:237–243. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2019.05.051. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources