Biological control of potato common scab and growth promotion of potato by Bacillus velezensis Y6
- PMID: 38149275
- PMCID: PMC10750399
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1295107
Biological control of potato common scab and growth promotion of potato by Bacillus velezensis Y6
Abstract
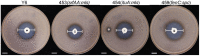
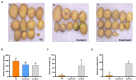
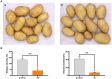
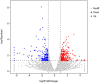
Potato common scab, caused mainly by Streptomyces scabies, causes surface necrosis and reduces the economic value of potato tubers, but effective chemical control is still lacking. In this study, an attempt was made to control potato common scab by inoculating potatoes with Bacillus velezensis (B. velezensis) and to further investigate the mechanism of biological control. The results showed that B. velezensis Y6 could reduce the disease severity of potato common scab from 49.92 ± 25.74% [inoculated with Streptomyces scabies (S. scabies) only] to 5.56 ± 1.89% (inoculated with S. scabies and Y6 on the same day) and increase the potato yield by 37.32% compared with the control under pot experiment in this study. Moreover, in the field trial, it was found that Y6 could also significantly reduce disease severity from 13.20 ± 1.00% to 4.00 ± 0.70% and increase the potato yield from 2.07 ± 0.10 ton/mu to 2.87 ± 0.28 ton/mu (p < 0.01; Tukey's test). Furthermore, RNA-seq analysis indicated that 256 potato genes were upregulated and 183 potato genes were downregulated in response to B. velezensis Y6 inoculation. In addition, strain Y6 was found to induce the expression of plant growth-related genes in potato, including cell wall organization, biogenesis, brassinosteroid biosynthesis, and plant hormone transduction genes, by 1.01-4.29 times. As well as up-regulate hydroquinone metabolism-related genes and several transcription factors (bHLH, MYB, and NAC) by 1.13-4.21 times. In summary, our study will help to understand the molecular mechanism of biological control of potato common scab and improve potato yield.
Keywords: Bacillus velezensis; Streptomyces scabies; antagonism; lipopeptide; potato; transcriptome.
Copyright © 2023 Tao, Wang, Li, Li, Cai, Zhao, Wang, Zeng, Qin, Xiong and Cai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Bacillus velezensis K-9 as a Potential Biocontrol Agent for Managing Potato Scab.Plant Dis. 2023 Dec;107(12):3943-3951. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-12-22-2829-RE. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Plant Dis. 2023. PMID: 37337440
-
Biological control of potato common scab by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba01.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 26;13(4):e0196520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196520. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29698535 Free PMC article.
-
Surfactin secreted by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba01 is required to combat Streptomyces scabies causing potato common scab.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Nov 1;13:998707. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.998707. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36388520 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and identification of an endophytic bacteria Bacillus sp. K-9 exhibiting biocontrol activity against potato common scab.Arch Microbiol. 2022 Jul 14;204(8):483. doi: 10.1007/s00203-022-02989-5. Arch Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35833995 Review.
-
Genetic and physiological determinants of Streptomyces scabies pathogenicity.Mol Plant Pathol. 2009 Sep;10(5):579-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2009.00561.x. Mol Plant Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19694949 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic and Antioxidant Responses of Different Control Methods to the Interaction of Sorghum sudangrass hybrids-Colletotrichum boninense.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 31;25(17):9505. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179505. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273450 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus and Paenibacillus as plant growth-promoting bacteria in soybean and cannabis.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jun 2;16:1529859. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1529859. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40525084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of plant transcription factors and priming of stress tolerance by plant growth-promoting bacteria: a systematic review.Ann Bot. 2025 Feb 19;135(3):387-402. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcae166. Ann Bot. 2025. PMID: 39279216
-
Biocontrol Effect of Bacillus velezensis D7-8 on Potato Common Scab and Its Complete Genome Sequence Analysis.Microorganisms. 2025 Mar 28;13(4):770. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040770. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284607 Free PMC article.
-
IAA Synthesis Pathway of Fitibacillus barbaricus WL35 and Its Regulatory Gene Expression Levels in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.).Microorganisms. 2024 Jul 26;12(8):1530. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081530. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batool T., Ali S., Seleiman M. F., Naveed N. H., Ali A., Ahmed K., et al. . (2020). Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria alleviates drought stress in potato in response to suppressive oxidative stress and antioxidant enzymes activities. Sci. Rep. 10:16975. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73489-z, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Braun S., Gevens A., Charkowski A., Allen C., Jansky S. (2017). Potato common scab: a review of the causal pathogens, management practices, varietal resistance screening methods, and host resistance. Am. J. Potato Res. 94, 283–296. doi: 10.1007/s12230-017-9575-3 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

