The Nucleosome Remodelling and Deacetylation complex coordinates the transcriptional response to lineage commitment in pluripotent cells
- PMID: 38149716
- PMCID: PMC10836651
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.060101
The Nucleosome Remodelling and Deacetylation complex coordinates the transcriptional response to lineage commitment in pluripotent cells
Abstract
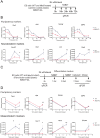
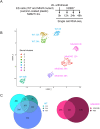
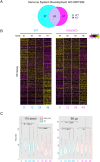
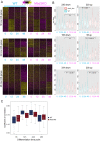
As cells exit the pluripotent state and begin to commit to a specific lineage they must activate genes appropriate for that lineage while silencing genes associated with pluripotency and preventing activation of lineage-inappropriate genes. The Nucleosome Remodelling and Deacetylation (NuRD) complex is essential for pluripotent cells to successfully undergo lineage commitment. NuRD controls nucleosome density at regulatory sequences to facilitate transcriptional responses, and also has been shown to prevent unscheduled transcription (transcriptional noise) in undifferentiated pluripotent cells. How these activities combine to ensure cells engage a gene expression program suitable for successful lineage commitment has not been determined. Here, we show that NuRD is not required to silence all genes. Rather, it restricts expression of genes primed for activation upon exit from the pluripotent state, but maintains them in a transcriptionally permissive state in self-renewing conditions, which facilitates their subsequent activation upon exit from naïve pluripotency. We further show that NuRD coordinates gene expression changes, which acts to maintain a barrier between different stable states. Thus NuRD-mediated chromatin remodelling serves multiple functions, including reducing transcriptional noise, priming genes for activation and coordinating the transcriptional response to facilitate lineage commitment.
Keywords: Chromatin; Embryonic stem cell; Lineage commitment; MBD3; NuRD; Transcription.
© 2024. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests Sara-Jane Dunn was an employee at Microsoft Research during this study and is currently employed at DeepMind. Neither Microsoft Research nor DeepMind have directed any aspect of the study nor exerted any commercial rights over the results. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential regulation of lineage commitment in human and mouse primed pluripotent stem cells by the nucleosome remodelling and deacetylation complex.Stem Cell Res. 2020 Jul;46:101867. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2020.101867. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Stem Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32535494 Free PMC article.
-
NuRD suppresses pluripotency gene expression to promote transcriptional heterogeneity and lineage commitment.Cell Stem Cell. 2012 May 4;10(5):583-94. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.02.020. Cell Stem Cell. 2012. PMID: 22560079 Free PMC article.
-
The methyl binding domain 3/nucleosome remodelling and deacetylase complex regulates neural cell fate determination and terminal differentiation in the cerebral cortex.Neural Dev. 2015 May 2;10:13. doi: 10.1186/s13064-015-0040-z. Neural Dev. 2015. PMID: 25934499 Free PMC article.
-
The Mi-2/NuRD complex: a critical epigenetic regulator of hematopoietic development, differentiation and cancer.Epigenetics. 2009 Nov 16;4(8):532-6. doi: 10.4161/epi.4.8.10108. Epub 2009 Nov 16. Epigenetics. 2009. PMID: 19923891 Review.
-
Mi-2/NuRD chromatin remodeling complexes regulate B and T-lymphocyte development and function.Immunol Rev. 2014 Sep;261(1):126-40. doi: 10.1111/imr.12209. Immunol Rev. 2014. PMID: 25123281 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction and regulatory expression of Polycomb and NuRD complexes in mouse embryonic stem cell under PKC inhibition.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 26;15(1):27204. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12427-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40715296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basu, S., Shukron, O., Hall, D., Parutto, P., Ponjavic, A., Shah, D., Boucher, W., Lando, D., Zhang, W., Reynolds, N.et al. (2023). Live-cell three-dimensional single-molecule tracking reveals modulation of enhancer dynamics by NuRD. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 30, 1628-1639. 10.1038/s41594-023-01095-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bornelöv, S., Reynolds, N., Xenophontos, M., Gharbi, S., Johnstone, E., Floyd, R., Ralser, M., Signolet, J., Loos, R., Dietmann, S.et al. (2018). The nucleosome remodeling and deacetylation complex modulates chromatin structure at sites of active transcription to fine-tune gene expression. Mol. Cell 71, 56-72.e4. 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burgold, T., Barber, M., Kloet, S., Cramard, J., Gharbi, S., Floyd, R., Kinoshita, M., Ralser, M., Vermeulen, M., Reynolds, N.et al. (2019). The Nucleosome Remodelling and Deacetylation complex suppresses transcriptional noise during lineage commitment. EMBO J. 38, e100788. 10.15252/embj.2018100788 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

