Severity of coronary artery disease is associated with diminished circANRIL expression: A possible blood based transcriptional biomarker in East Africa
- PMID: 38149798
- PMCID: PMC10844708
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.18093
Severity of coronary artery disease is associated with diminished circANRIL expression: A possible blood based transcriptional biomarker in East Africa
Abstract
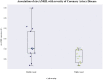
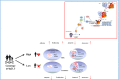
Antisense Noncoding RNA in the INK4 Locus (ANRIL) is the prime candidate gene at Chr9p21, the well-defined genetic risk locus associated with coronary artery disease (CAD). ANRIL and its transcript variants were investigated for the susceptibility to CAD in adipose tissues (AT) and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of the study group and the impact of 9p21.3 locus mutations was further analysed. Expressions of ANRIL, circANRIL (hsa_circ_0008574), NR003529, EU741058 and DQ485454 were detected in epicardial AT (EAT) mediastinal AT (MAT), subcutaneous AT (SAT) and PBMCs of CAD patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting and non-CAD patients undergoing heart valve surgery. ANRIL expression was significantly upregulated, while the expression of circANRIL was significantly downregulated in CAD patients. Decreased circANRIL levels were significantly associated with the severity of CAD and correlated with aggressive clinical characteristics. rs10757278 and rs10811656 were significantly associated with ANRIL and circANRIL expressions in AT and PBMCs. The ROC-curve analysis suggested that circANRIL has high diagnostic accuracy (AUC: 0.9808, cut-off: 0.33, sensitivity: 1.0, specificity: 0.88). circANRIL has high diagnostic accuracy (AUC: 0.9808, cut-off: 0.33, sensitivity: 1.0, specificity: 0.88). We report the first data demonstrating the presence of ANRIL and its transcript variants expressions in the AT and PBMCs of CAD patients. circANRIL having a synergetic effect with ANRIL plays a protective role in CAD pathogenesis. Therefore, altered circANRIL expression may become a potential diagnostic transcriptional biomarker for early CAD diagnosis.
Keywords: 9p21.3; ANRIL; circANRIL; coronary artery disease; hsa_circ_0008574; peripheral mononuclear blood cells; polymorphism; transcriptional biomarker; visceral adipose tissue.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Janssen I, Katzmarzyk PT, Ross R. Body mass index, waist circumference, and health risk: evidence in support of current national institutes of health guidelines. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:2074‐2079. - PubMed
-
- Iacobellis G, Ribaudo MC, Assael F, et al. Echocardiographic epicardial adipose tissue is related to anthro‐pometric and clinical parameters of metabolic syndrome: a new indicator of cardiovascular risk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:5163‐5168. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

