How New Developments in Pharmacology Receptor Theory Are Changing (Our Understanding of) Hypertension Therapy
- PMID: 38150382
- PMCID: PMC10941088
- DOI: 10.1093/ajh/hpad121
How New Developments in Pharmacology Receptor Theory Are Changing (Our Understanding of) Hypertension Therapy
Abstract
Background: Many hypertension therapeutics were developed prior to major advances in drug receptor theory. Moreover, newer drugs may take advantage of some of the newly understood modalities of receptor function.
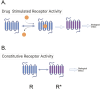
Goal: The goal of this review is to provide an up-to-date summary of drug receptor theory. This is followed by a discussion of the drug classes recognized for treating hypertension to which new concepts in receptor theory apply.
Results: We raise ideas for mechanisms of potential new antihypertensive drugs and whether they may take advantage of new theories in drug-receptor interaction.
Keywords: agonist; antagonist; blood pressure; constitutive activity; drug receptor theory; drug–receptor interaction; hypertension; inverse agonist.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Journal of Hypertension, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
SWW and RRN declare no conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise. RRT: Consultant to Medtronic, Cytel, Regeneron, Backbeat Orchestra and Novartis. Royalty income from UpToDate.
Figures




References
-
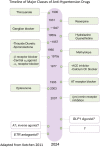
- Kotchen TA. Historical trends and milestones in hypertension research. Hypertension 2011; 58:522–538. - PubMed
-
- Moser M. Myths, Misconceptions and Heroics: The Story of the Treatment of Hypertension from the 1930s. Le Jacq Communications: Greenwich, CT, 1997.
-
- Lyons HH, Hoobler SW, Neligh RB, Moe GK, Peet MM.. Experiences with tetraethylammonium chloride in hypertension. JAMA 1948; 136:608–613. - PubMed
-
- Beyer KH. Chlorothiazide; how the thiazides evolved as antihypertensive therapy. Hypertension 1993; 22:388–391. - PubMed
-
- Kenakin TP. A Pharmacology Primer; Techniques for More Effective and Strategic Drug Discovery, 6th edn. San Diego CA USA: Academic Press, Elsevier, 2022
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

