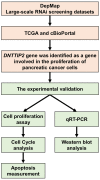
Depletion of DNTTIP2 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
- PMID: 38151292
- PMCID: PMC10756344
- DOI: 10.21873/cgp.20426
Depletion of DNTTIP2 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
Abstract
Background/aim: Pancreatic cancer is one of the most lethal malignant cancers worldwide and the seventh most common cause of cancer-related death in both sexes. Herein, we analyzed open access data and discovered that expression of a gene called deoxynucleotidyltransferase terminal-interacting protein 2 (DNTTIP2) is linked to prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). We then elucidated the role of DNTTIP2 in the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro.
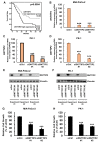
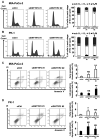
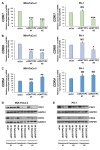
Materials and methods: A WST-8 assay, cell cycle analysis, Annexin-V staining, quantitative reverse transcription-PCR, and western blot analysis were conducted to assess cell proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, and expression of DNTTIP2 mRNA and protein, respectively, in DNTTIP2-depleteted MIA-PaCa-2 and PK-1 cells.
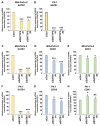
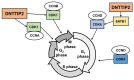
Results: Depletion of DNTTIP2 induced G1 arrest in MIA-PaCa-2 cells by decreasing expression of special AT-rich sequence binding protein 1 (SATB1) and cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6). In addition, depletion of DNTTIP2 induced G2 arrest in PK-1 cells by decreasing expression of CDK1. Depletion of DNTTIP2 did not induce apoptosis in MIA-PaCa-2 or PK-1 cells.
Conclusion: DNTTIP2 is involved in proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Thus, DNTTIP2 is a potential target for inhibiting progression of pancreatic cancers.
Keywords: CDK1; CDK6; DNTTIP2; Pancreatic cancer; SATB1; cells.
Copyright © 2024, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of Hematopoietic Pre-B-cell Leukemia Transcription Factor Interacting Protein Knockdown on Proliferation,Cell Cycle and Apoptosis in Pancreatic Cancer Cells].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2020 Feb 28;42(1):7-15. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.11192. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32131934 Chinese.
-
HOXB7 mRNA is overexpressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas and its knockdown induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.BMC Cancer. 2013 Oct 2;13:451. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-451. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24088503 Free PMC article.
-
[MiR-150-5p inhibits the proliferation and promoted apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Jul;42(7):460-4. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5807.2013.07.007. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24246865 Chinese.
-
RACK1 overexpression associates with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma growth and poor prognosis.Exp Mol Pathol. 2016 Oct;101(2):176-186. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2016.08.001. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Exp Mol Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27498047
-
An increased expression of long non-coding RNA PANDAR promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Nov;95:685-691. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.124. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28886528
Cited by
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx)-mediated immune modulation and prognostic model development in hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 27;20(6):e0325363. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325363. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40577282 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane regulates cell proliferation and induces apoptotic cell death mediated by ROS-cell cycle arrest in pancreatic cancer cells.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 29;14:1442737. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1442737. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39267822 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing Plant Flavonoids to Fight Pancreatic Cancer.Curr Nutr Rep. 2024 Sep;13(3):566-581. doi: 10.1007/s13668-024-00545-9. Epub 2024 May 3. Curr Nutr Rep. 2024. PMID: 38700837 Review.
-
SATB1 in cancer progression and metastasis: mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 25;15:1535929. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1535929. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40071088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
