Obesity-induced PARIS (ZNF746) accumulation in adipose progenitor cells leads to attenuated mitochondrial biogenesis and impaired adipogenesis
- PMID: 38151567
- PMCID: PMC10752882
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-49996-0
Obesity-induced PARIS (ZNF746) accumulation in adipose progenitor cells leads to attenuated mitochondrial biogenesis and impaired adipogenesis
Abstract
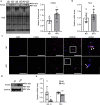
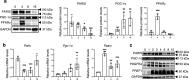
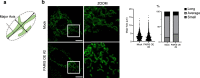
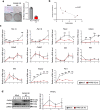
White adipose tissue (WAT) is critical for whole-body energy metabolism, and its dysfunction leads to various metabolic disorders. In recent years, many studies have suggested that impaired mitochondria may contribute to obesity-related decline in adipose tissue function, but the detailed mechanisms remain unclear. To investigate these mechanisms, we carried out a comprehensive analysis of WAT from mice with diet-induced obesity. We discovered the transcription factor Parkin interactive substrate (PARIS or ZNF746), which suppresses the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α), a key regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis, to be accumulated in adipose progenitor cells from obese mice. Furthermore, we demonstrated that 3T3-L1 preadipocytes with overexpression of PARIS protein exhibited decreased mitochondrial biogenesis and impaired adipogenesis. Our results suggest that the accumulation of PARIS protein may be a novel component in the pathogenesis of obesity-related dysfunction in WAT.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

