Preoperatively administered single dose of dexketoprofen decreases pain intensity on the first 5 days after craniotomy: A single-centre placebo-controlled, randomized trial
- PMID: 38152091
- PMCID: PMC10751892
- DOI: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0323
Preoperatively administered single dose of dexketoprofen decreases pain intensity on the first 5 days after craniotomy: A single-centre placebo-controlled, randomized trial
Abstract
Background and purpose: Headache attributed to craniotomy is an underestimated and under-treated condition. Previous studies confirmed the efficacy of preemptive analgesia with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents. The aim of the present work was to test the hypothesis of whether a single preoperatively administered dose of dexketoprofen (DEX) has the potency to decrease postcraniotomy headache (PCH) as compared to placebo (PL).
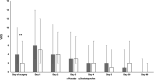
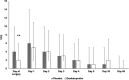
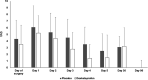
Patients and methods: This is a single-centre, randomized, PL-controlled trial comparing the effect of a single oral dose of 25 mg DEX to PL on the intensity of PCH. Patients undergoing craniotomy were randomly allocated to DEX and PL groups. Patients rated their actual and worst daily pain using visual analogue scale (VAS) scores during intrahospital treatment (0-5 days) and 30 and 90 days postoperatively.
Results: Two hundred patients were included. DEX decreased the worst daily pain intensity in the first 24 h only; the 5-days cumulative score of actual pain was 9.7 ± 7.9 cm for the DEX group and 12.6 ± 10.5 cm for the PL group, respectively (p = 0.03). This difference disappeared in the late, 30-, and 90-day follow-up period. No differences in VAS scores could be detected in supra- and infratentorial cases among the DEX and PL groups.
Conclusions: A single preoperative dose of 25 mg of DEX slightly decreases the intensity of PCH in the first 5 days after craniotomy but it does not have an effect on chronic headaches and postoperative analgesic requirements.
Keywords: dexketoprofen; postcraniotomy headache; preemptive analgesia.
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders. 3rd edn. Cephalalgia. Vol. 38. 2018. p. 1–211. - PubMed
-
- Rocha-Filho PA, Gherpelli JL, de Siqueira JT, Rabello GD. Post- craniotomy headache: characteristics, behaviour and effect on quality of life in patients operated for treatment of supratentorial intracranial aneurysms. Cephalalgia: Int J Headache. 2008;28:41–8. - PubMed
-
- Molnár L, Simon É, Nemes R, Fülesdi B, Molnár C. Postcraniotomy headache. J Anesth. 2014;28:102–11. - PubMed
-
- De Benedittis G, Lorenzetti A, Migliore M, Spagnoli D, Tiberio F, Villani RM. Postoperative pain in neurosurgery: a pilot study in brain surgery. Neurosurgery. 1996;38:466–9. - PubMed
-
- Molnár C, Simon É, Kazup Á, Gál J, Molnár L, Novák L, et al. A single preoperative dose of diclofenac reduces the intensity of acute postcraniotomy headache and decreases analgesic requirements over five postoperative days in adults: A single-center, randomized, blinded trial. J Neurol Sci. 2015;353:70–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
