Engineered Exosome for Drug Delivery: Recent Development and Clinical Applications
- PMID: 38152837
- PMCID: PMC10752020
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S444582
Engineered Exosome for Drug Delivery: Recent Development and Clinical Applications
Abstract
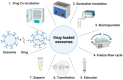
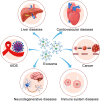
Exosomes are nano-sized membrane vesicles that transfer bioactive molecules between cells and modulate various biological processes under physiological and pathological conditions. By applying bioengineering technologies, exosomes can be modified to express specific markers or carry therapeutic cargo and emerge as novel platforms for the treatment of cancer, neurological, cardiovascular, immune, and infectious diseases. However, there are many challenges and uncertainties in the clinical translation of exosomes. This review aims to provide an overview of the recent advances and challenges in the translation of engineered exosomes, with a special focus on the methods and strategies for loading drugs into exosomes, the pros and cons of different loading methods, and the optimization of exosome production based on the drugs to be encapsulated. Moreover, we also summarize the current clinical applications and prospects of engineered exosomes, as well as the potential risks and limitations that need to be addressed in exosome engineering, including the standardization of exosome preparation and engineering protocols, the quality and quantity of exosomes, the control of drug release, and the immunogenicity and cytotoxicity of exosomes. Overall, engineered exosomes represent an exciting frontier in nanomedicine, but they still face challenges in large-scale production, the maintenance of storage stability, and clinical translation. With continuous advances in this field, exosome-based drug formulation could offer great promise for the targeted treatment of human diseases.
Keywords: clinical application; drug delivery; engineered exosomes; preparation strategy.
© 2023 Tian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Engineering Approaches for Exosome Cargo Loading and Targeted Delivery: Biological versus Chemical Perspectives.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024 Oct 14;10(10):5960-5976. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.4c00856. Epub 2024 Jun 28. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024. PMID: 38940421 Review.
-
Exosomes in cancer nanomedicine: biotechnological advancements and innovations.Mol Cancer. 2025 Jun 7;24(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02372-0. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40481526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome-like systems: Nanotechnology to overcome challenges for targeted cancer therapies.Cancer Lett. 2023 May 1;561:216151. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216151. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 37001751 Review.
-
Exosome engineering for efficient and targeted drug delivery: Current status and future perspective.J Physiol. 2023 Nov;601(22):4853-4872. doi: 10.1113/JP282799. Epub 2022 Jun 2. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 35570717 Review.
-
Exosome-based nanocarriers as bio-inspired and versatile vehicles for drug delivery: recent advances and challenges.J Mater Chem B. 2019 Apr 21;7(15):2421-2433. doi: 10.1039/c9tb00170k. Epub 2019 Mar 13. J Mater Chem B. 2019. PMID: 32255119 Review.
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in joint diseases: Therapeutic effects and underlying mechanisms.J Orthop Translat. 2024 Jul 27;48:53-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.07.005. eCollection 2024 Sep. J Orthop Translat. 2024. PMID: 39170747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of exosomes in modulating non-small cell lung cancer radiosensitivity.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 16;15:1471476. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1471476. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39737074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal BMPR2 Macromolecule Facilitates Alveolar Epithelial Cell Repair Through Functional Complex Formation with BMPR1B in Acute Lung Injury.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jun 7;20:7233-7249. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S519393. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40502982 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting secretory autophagy in solid cancers: mechanisms, immune regulation and clinical insights.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025 Feb 1;14(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40164-025-00603-0. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39893499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes in neurodegenerative diseases: Therapeutic potential and modification methods.Neural Regen Res. 2026 Feb 1;21(2):478-490. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00720. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Neural Regen Res. 2026. PMID: 40326981 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

