Streptococcus suis serotype 9 in Italy: genomic insights into high-risk clones with emerging resistance to penicillin
- PMID: 38153239
- PMCID: PMC10832592
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkad395
Streptococcus suis serotype 9 in Italy: genomic insights into high-risk clones with emerging resistance to penicillin
Abstract
Background: Streptococcus suis is an important pig pathogen and an emerging zoonotic agent. In a previous study, we described a high proportion of penicillin-resistant serotype 9 S. suis (SS9) isolates on pig farms in Italy.
Objectives: We hypothesized that resistance to penicillin emerged in some SS9 lineages characterized by substitutions at the PBPs, contributing to the successful spread of these lineages in the last 20 years.
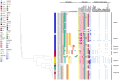
Methods: Sixty-six SS9 isolates from cases of streptococcosis in pigs were investigated for susceptibility to penicillin, ceftiofur and ampicillin. The isolates were characterized for ST, virulence profile, and antimicrobial resistance genes through WGS. Multiple linear regression models were employed to investigate the associations between STs, year of isolation, substitutions at the PBPs and an increase in MIC values to β-lactams.
Results: MIC values to penicillin increased by 4% each year in the study period. Higher MIC values for penicillin were also positively associated with ST123, ST1540 and ST1953 compared with ST16. The PBP sequences presented a mosaic organization of blocks. Within the same ST, substitutions at the PBPs were generally more frequent in recent isolates. Resistance to penicillin was driven by substitutions at PBP2b, including K479T, D512E and K513E, and PBP2x, including T551S, while reduced susceptibility to ceftiofur and ampicillin were largely dependent on substitutions at PBP2x.
Conclusions: Here, we identify the STs and substitutions at the PBPs responsible for increased resistance of SS9 to penicillin on Italian pig farms. Our data highlight the need for monitoring the evolution of S. suis in the coming years.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

