The mediation and interaction of the obesity index between moderate-vigorous recreational physical activity and hypertension
- PMID: 38153927
- PMCID: PMC10754462
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296333
The mediation and interaction of the obesity index between moderate-vigorous recreational physical activity and hypertension
Abstract
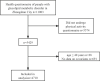
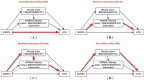
Previous studies showed that physical activity (PA) is concerned with hypertension (HTN). However, the mediation and interaction role of the obesity index: body mass index (BMI), waist-hip ratio (WHR), body fat rate (BFR) and visceral fat index (VFI) between PA and HTN has never been studied. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to assess the mediation and interaction of the obesity index between moderate-vigorous recreational physical activity (MVRPA) and HTN. We conducted a cross-sectional study of 4710 individuals aged 41 or older in Torch Development Zone, Zhongshan City. The mediation and interaction of the obesity index were evaluated by a four-way decomposition. 48.07% of participants had HTN among these groups. In the adjusted linear regression model, MVRPA was significantly correlated with WHR (β±SE = -0.005±0.002; P<0.05). Compared to sufficient MVRPA (odds ratio (OR) = 1.35), 95% (confidence interval (CI) = 1.17-1.56), insufficient MVRPA increased the risk of developing HTN. Furthermore, there were associations between BMI, WHR, BFR, VFI and HTN where the adjusted ORs and 95% CIs were 1.11 (1.09-1.13), 6.23 (2.61-14.90), 1.04 (1.03-1.06), 1.07 (1.06-1.09), respectively. The mediation analyses suggested that the impact of MVRPA on HTN risk may partly be explained by changes in obesity index, with a pure indirect mediation of WHR between MVRPA and HTN (P<0.05). Therefore, weight control, especially reducing abdominal obesity and maintaining adequate MVRPA, may lead to more proper control of HTN.
Copyright: © 2023 Du et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Different Obesity Indices for Predicting Incident Hypertension.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2017 Jun;24(2):157-166. doi: 10.1007/s40292-017-0186-3. Epub 2017 Feb 4. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2017. PMID: 28160265
-
Cut-off points for anthropometric indices to screen for hypertension among Iranian adults of the Bandare-Kong cohort: a cross-sectional study.BMC Public Health. 2022 Nov 11;22(1):2064. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-14489-8. BMC Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36369024 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between obesity indices and hypertension among middle-aged and elderly populations in Taiwan: a community-based, cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2019 Oct 28;9(10):e031660. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031660. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31662394 Free PMC article.
-
Anthropometric and metabolic indicators in hypertensive patients.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2009 Jul;19(7):421-7. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2009. PMID: 19576149
-
Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension in Adolescents with Obesity.Curr Cardiovasc Risk Rep. 2024;18(8-9):115-124. doi: 10.1007/s12170-024-00740-x. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Curr Cardiovasc Risk Rep. 2024. PMID: 39105085 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optical Marker-Based Motion Capture of the Human Spine: A Scoping Review of Study Design and Outcomes.Ann Biomed Eng. 2024 Sep;52(9):2373-2387. doi: 10.1007/s10439-024-03567-0. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Ann Biomed Eng. 2024. PMID: 39023832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu X, Byles J, Shi Z, McElduff P, Hall J. Dietary pattern transitions, and the associations with BMI, waist circumference, weight and hypertension in a 7-year follow-up among the older Chinese population: a longitudinal study. BMC Public Health. 2016;16:743–754. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-3425-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

