Cooled radiofrequency ablation of genicular nerves for knee osteoarthritis
- PMID: 38155108
- PMCID: PMC10764214
- DOI: 10.3344/kjp.23344
Cooled radiofrequency ablation of genicular nerves for knee osteoarthritis
Abstract
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a prevalent and debilitating musculoskeletal condition that significantly affects the quality of life of millions of individuals worldwide. In recent years, cooled radiofrequency ablation (CRFA) has become a viable treatment option for knee OA. This review thoroughly evaluated the existing literature on CRFA therapy for knee OA. It delved into the mechanisms behind CRFA, evaluated its clinical efficacy, and investigated potential avenues for future research and application. The insights gained from this review are crucial for healthcare professionals, researchers, and policymakers, offering an updated perspective on CRFA's role as a viable therapeutic option for knee OA.
Keywords: Chronic Pain; Cooled Radiofrequency Ablation; Denervation; Hyaluronic Acid; Injections; Intra-Articular; Knee; Osteoarthritis; Radiofrequency Ablation; Steroids; Treatment Outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
Jin-Woo Shin is an editorial board member, and Seong-Soo Choi is a section editor of the Korean Journal of Pain; however, they have not been involved in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process of this article. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

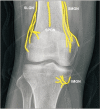

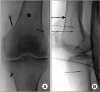
References
-
- Bunt CW, Jonas CE, Chang JG. Knee pain in adults and adolescents: the initial evaluation. Am Fam Physician. 2018;98:576–85. - PubMed
-
- Jones BQ, Covey CJ, Sineath MH., Jr Nonsurgical management of knee pain in adults. Am Fam Physician. 2015;92:875–83. - PubMed
-
- Skou ST, Roos EM, Simonsen O, Laursen MB, Rathleff MS, Arendt-Nielsen L, et al. The efficacy of non-surgical treatment on pain and sensitization in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a pre-defined ancillary analysis from a randomized controlled trial. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24:108–16. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2015.07.013. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

