Identification of CD38, CD97, and CD278 on the HIV surface using a novel flow virometry screening assay
- PMID: 38155248
- PMCID: PMC10754950
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-50365-0
Identification of CD38, CD97, and CD278 on the HIV surface using a novel flow virometry screening assay
Abstract
While numerous cellular proteins in the HIV envelope are known to alter virus infection, methodology to rapidly phenotype the virion surface in a high throughput, single virion manner is lacking. Thus, many human proteins may exist on the virion surface that remain undescribed. Herein, we developed a novel flow virometry screening assay to discover new proteins on the surface of HIV particles. By screening a CD4+ T cell line and its progeny virions, along with four HIV isolates produced in primary cells, we discovered 59 new candidate proteins in the HIV envelope that were consistently detected across diverse HIV isolates. Among these discoveries, CD38, CD97, and CD278 were consistently present at high levels on virions when using orthogonal techniques to corroborate flow virometry results. This study yields new discoveries about virus biology and demonstrates the utility and feasibility of a novel flow virometry assay to phenotype individual virions.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
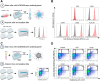

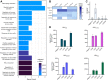


References
-
- Bounou S, Leclerc JE, Tremblay MJ. Presence of host ICAM-1 in laboratory and clinical strains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 increases virus infectivity and CD4+-T-cell depletion in human lymphoid tissue, a major site of replication in vivo. J. Virol. 2002;76:1004–1014. doi: 10.1128/JVI.76.3.1004-1014.2002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

