Multi-ancestry genome-wide association meta-analysis of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 38155330
- PMCID: PMC10786718
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-023-01584-8
Multi-ancestry genome-wide association meta-analysis of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
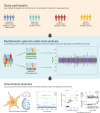
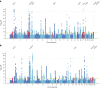
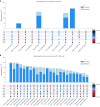
Although over 90 independent risk variants have been identified for Parkinson's disease using genome-wide association studies, most studies have been performed in just one population at a time. Here we performed a large-scale multi-ancestry meta-analysis of Parkinson's disease with 49,049 cases, 18,785 proxy cases and 2,458,063 controls including individuals of European, East Asian, Latin American and African ancestry. In a meta-analysis, we identified 78 independent genome-wide significant loci, including 12 potentially novel loci (MTF2, PIK3CA, ADD1, SYBU, IRS2, USP8, PIGL, FASN, MYLK2, USP25, EP300 and PPP6R2) and fine-mapped 6 putative causal variants at 6 known PD loci. By combining our results with publicly available eQTL data, we identified 25 putative risk genes in these novel loci whose expression is associated with PD risk. This work lays the groundwork for future efforts aimed at identifying PD loci in non-European populations.
© 2023. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
K.H. and members of the 23andMe Research Team are employed by and hold stock or stock options in 23andMe. M.A.N.’s participation in this project was part of a competitive contract awarded to Data Tecnica International by the NIH to support open science research; he also currently serves on the scientific advisory board for Clover Therapeutics and is an advisor to Neuron23. A.J.N. reports consultancy and personal fees from AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Profile, Roche, Biogen, UCB, Bial, Charco Neurotech, uMedeor, Alchemab and Britannia outside the submitted work. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

