Expression of HIF-1α in pediatric asthmatic patients
- PMID: 38155704
- PMCID: PMC10715186
- DOI: 10.4081/mrm.2023.927
Expression of HIF-1α in pediatric asthmatic patients
Abstract
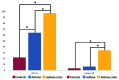
Background: Several studies have suggested that HIF-1α regulates eosinophil activity and induces epithelial inflammation via NF-κB activation in the pathophysiology of asthma. The purpose of this study was to examine the expression of the transcription factors HIF-1α and nuclear HIF in mononuclear cells obtained from peripheral blood samples of healthy pediatric patients, asthmatic patients, and asthmatic exacerbations, regardless of disease severity.
Methods: HIF-1 levels were measured using immunocytochemistry in 133 patients aged 6 to 17 years in this crosssectional and comparative study. A microscope was used to examine glass slides, and positive cells were counted in four fields per slide using an image analyzer.
Results: HIF-1α and nuclear HIF levels were significantly higher in asthma patients and even higher in patients experiencing asthma attacks (p<0.0001, 95% CI). There was no significant difference in the percentage of HIF-1α expression between groups with intermittent asthma and those with mild persistent asthma, nor between patients with asthma and those experiencing asthma exacerbations.
Conclusions: When compared to healthy individuals, the expression of nuclear HIF and HIF-1α is increased in peripheral mononuclear cells in asthma patients and even more so in asthma exacerbations. This suggests that HIF-1α is important in the pathogenesis of this disease.
Keywords: HIF-1α; airway remodelling; asthma; asthmatic exacerbation; pediatric.
Copyright © 2023, the Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have no disclosures, relevant financial relationships, patents, or conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-1β upregulates Muc5ac expression via NF-κB-induced HIF-1α in asthma.Immunol Lett. 2017 Dec;192:20-26. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2017.10.006. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Immunol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29031476
-
The YAP/HIF-1α/miR-182/EGR2 axis is implicated in asthma severity through the control of Th17 cell differentiation.Cell Biosci. 2021 May 12;11(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00560-1. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33980319 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of budesonide on HIF-1α and VEGF expression and airway remodeling in an asthmatic mouse model].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2012 Aug;14(8):622-7. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22898286 Chinese.
-
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia-inducible factor in the airway of asthmatic patients.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006 Dec;97(6):794-9. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)60971-4. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17201239
-
[Contribution of hypoxia in pulmonary tissue remodeling in asthmatic processes].Rev Alerg Mex. 2008 Jan-Feb;55(1):18-32. Rev Alerg Mex. 2008. PMID: 18697450 Review. Spanish.
References
-
- Papi A, Brightling C, Pedersen SE, Reddel HK. Seminar asthma. Lancet 2022;391:783-800. - PubMed
-
- Stern J, Pier J, Litonjua AA. Asthma epidemiology and risk factors. Semin Immunopathol 2020;42:5-15. - PubMed
-
- Hammad H, Lambrecht BN. The basic immunology of asthma. Cell 2021;184:1469-85. - PubMed
-
- Pałgan K, Bartuzi Z. Angiogenesis in bronchial asthma. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 2015;28:415-20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources