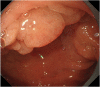
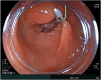
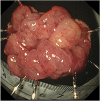
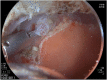
Endoscopic submucosal dissection for a duodenal polyp at the upper aspect of the duodenal bulb using a newly developed endoscope
- PMID: 38155827
- PMCID: PMC10751466
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vgie.2023.07.016
Endoscopic submucosal dissection for a duodenal polyp at the upper aspect of the duodenal bulb using a newly developed endoscope
Conflict of interest statement
The authors did not disclose any financial relationships.
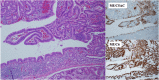
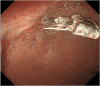
Figures


References
-
- Takinami M., Kakushima N., Yoshida M., et al. Endoscopic features of submucosal invasive non-ampullary duodenal carcinomas. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;35:821–826. - PubMed
-
- Shichijo S., Takeuchi Y., Matsuno K., et al. Pulley traction-assisted colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection: a retrospective case series. Dig Dis. 2019;37:473–477. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

