Durability of the Efficacy and Safety of Dolutegravir-Based and Low-Dose Efavirenz-Based Regimens for the Initial Treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection in Cameroon: Week 192 Data of the NAMSAL-ANRS-12313 Study
- PMID: 38156046
- PMCID: PMC10754645
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofad582
Durability of the Efficacy and Safety of Dolutegravir-Based and Low-Dose Efavirenz-Based Regimens for the Initial Treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection in Cameroon: Week 192 Data of the NAMSAL-ANRS-12313 Study
Abstract
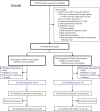
Background: A prospective study was extended to the new antiretroviral and monitoring strategies in HIV-infected adults in low-income countries (NAMSAL-ANRS)-12313 trial, a 96-week open-label, multicenter, randomized phase 3 trial comparing dolutegravir (DTG) 50 mg with efavirenz 400 mg (EFV400), both administered with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and lamivudine (TDF/3TC) as first-line treatment for antiretroviral therapy (ART)-naive people living with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV). Noninferiority of DTG to EFV400 was demonstrated at 48-week and sustained at 96 weeks. Here, we present results at 192-week.
Methods: Previous trial participants were reconsented and followed up on their initial randomization arm (1:1 DTG/TDF/3TC:EFV400/TDF/3TC). Assessments included changes in viral suppression, biological parameters, and new serious adverse events (SAEs).
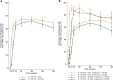
Results: Among the participants enrolled in the trial, 81% (499/613) were analyzed at week 192: 84% (261/310) on DTG/TDF/3TC and 78% (238/303) on EFV400/TDF/3TC. HIV RNA suppression was maintained in 69% (214/310) on DTG/TDF/3TC-based and 62% (187/303) on EFV400/TDF/3TC-based regimens (difference, 7.3% [95% confidence interval, -.20 to 14.83]; P = .057). Five (DTG/TDF/3TC = 2; EFV400/TDF/3TC = 3) new viral failures (World Health Organization definition) without related resistance DTG mutations and 24 new SAEs were observed (DTG/TDF/3TC = 13; EFV400/TDF/3TC = 11). Mean weight gain was +9.4 kg on DTG/TDF/3TC and +5.9 kg on EFV400/TDF/3TC. The percentage of participants with obesity increased from 6.9% to 27.7% on DTG/TDF/3TC (P < .0001) and from 8.3% to 16.7% on EFV400/TDF/3TC (P = .0033).
Conclusions: Four-year follow-up of people with HIV on DTG- and EFV400-based regimens showed long-term efficacy and safety of both ARTs, markedly among participants on DTG/TDF/3TC with high baseline viral load. However, unexpected substantial weight gain over time was prominent among participants on DTG/TDF/3TC, which should be closely monitored. Clinical Trials Registration. NCT02777229.
Keywords: HIV-1; dolutegravir; efficacy-durability; low-dose-efavirenz; weight gain.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. A. C. was a member of the WHO guideline panel in 2018 and 2019. The HIV Unit of Geneva University Hospitals (HUG) received unrestricted educational grants from ViiV, AbbVie, Gilead, and MSD, all of which also provided financial support to the LIPO group and metabolism (day hospital) in the HIV/AIDS Unit of HUG. J. R. has received personal fees and grants from Gilead, MSD, Pfizer, Tibotec-Janssen, and ViiV Healthcare for participation in advisory boards, educational programs, and conferences. All other authors report no potential conflicts.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) . Antiretroviral medicines in low- and middle-income countries: forecasts of global and regional demand for 2021–2025. 2022. Available at: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/352000. Accessed 30 May 2022.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Regional Office for Europe . Pocket book of primary health care for children and adolescents: guidelines for health promotion, disease prevention and management from the newborn period to adolescence. 2022. Available at: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/352485. Accessed 30 May 2022.
-
- Walmsley SL, Antela A, Clumeck N, et al. Dolutegravir plus abacavir–lamivudine for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. N Engl J Med 2013; 369:1807–18. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

