Maxillary Sinus Lift Procedures: An Overview of Current Techniques, Presurgical Evaluation, and Complications
- PMID: 38156177
- PMCID: PMC10753870
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.49553
Maxillary Sinus Lift Procedures: An Overview of Current Techniques, Presurgical Evaluation, and Complications
Abstract
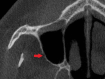
A maxillary sinus lift procedure is indicated if a dental implant needs to be placed in the posterior maxilla with limited bone available to accommodate a dental implant. Both open and closed sinus lifting procedures are reliable approaches for increasing the bone volume needed to support proper implant positioning. However, these methods can lead to several complications. In addition to the general complications commonly linked to oral surgery, such as swelling or hematoma, the primary complication in open sinus lifting is typically the perforation of the Schneiderian membrane during osteotomy. Detailed and extensive presurgical evaluation is crucial to minimize such complications. The objective of this study was to delineate contemporary trends in sinus lift surgery, with a specific emphasis on different techniques of sinus lift procedure, anatomical and surgical factors, presurgical evaluation, bone grafting, and the practical implications of these factors in implant dentistry cases involving a deficient posterior maxilla. In conclusion, while both osteotome and lateral window techniques can assist clinicians in addressing the complexities of implant placement in a deficient posterior maxilla, bone height before implantation remains a critical factor in determining the success and longevity of implants.
Keywords: anatomy; bone augmentation; complications; maxillary sinus; perforation; schneiderian membrane; sinus lifting procedure.
Copyright © 2023, Alshamrani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Sinus floor elevation utilizing the transalveolar approach. Pjetursson BE, Lang NP. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25123761/ Periodontol 2000. 2014;66:59–71. - PubMed
-
- Dimensional changes of the maxillary sinus following tooth extraction in the posterior maxilla with and without socket preservation. Levi I, Halperin-Sternfeld M, Horwitz J, Zigdon-Giladi H, Machtei EE. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2017;19:952–958. - PubMed
-
- Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone. Boyne PJ, James RA. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6993637/ J Oral Surg. 1980;38:613–616. - PubMed
-
- Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental implants. A systematic review. Wallace SS, Froum SJ. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14971260/ Ann Periodontol. 2003;8:328–343. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources