Advances in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease based on oral bacteria
- PMID: 38156323
- PMCID: PMC10754487
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1291455
Advances in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease based on oral bacteria
Abstract
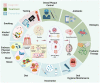
With the global population undergoing demographic shift towards aging, the prevalence of Alzheimer's disease (AD), a prominent neurodegenerative disorder that primarily afflicts individuals aged 65 and above, has increased across various geographical regions. This phenomenon is accompanied by a concomitant decline in immune functionality and oral hygiene capacity among the elderly, precipitating compromised oral functionality and an augmented burden of dental plaque. Accordingly, oral afflictions, including dental caries and periodontal disease, manifest with frequency among the geriatric population worldwide. Recent scientific investigations have unveiled the potential role of oral bacteria in instigating both local and systemic chronic inflammation, thereby delineating a putative nexus between oral health and the genesis and progression of AD. They further proposed the oral microbiome as a potentially modifiable risk factor in AD development, although the precise pathological mechanisms and degree of association have yet to be fully elucidated. This review summarizes current research on the relationship between oral bacteria and AD, describing the epidemiological and pathological mechanisms that may potentially link them. The purpose is to enrich early diagnostic approaches by incorporating emerging biomarkers, offering novel insights for clinicians in the early detection of AD. Additionally, it explores the potential of vaccination strategies and guidance for clinical pharmacotherapy. It proposes the development of maintenance measures specifically targeting oral health in older adults and advocates for guiding elderly patients in adopting healthy lifestyle habits, ultimately aiming to indirectly mitigate the progression of AD while promoting oral health in the elderly.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; anti-bacterial agents; dental prophylaxis; early diagnosis; healthy lifestyle; oral-gut-brain axis; probiotics; vaccine.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Mi, Ying, Lin and Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of the oral microbiome, host response, and periodontal disease treatment in Alzheimer's disease: A primer.Periodontol 2000. 2025 Jun 11. doi: 10.1111/prd.12631. Online ahead of print. Periodontol 2000. 2025. PMID: 40495582 Review.
-
Association between periodontitis and Alzheimer's disease: A narrative review.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025 Jan 17;18:360-365. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.12.004. eCollection 2025 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40060035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathophysiological association between periodontal disease and Alzheimer's disease: Importance of periodontal health in the elderly.J Oral Biosci. 2021 Dec;63(4):351-359. doi: 10.1016/j.job.2021.08.007. Epub 2021 Oct 9. J Oral Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34637820 Review.
-
Unlocking Modifiable Risk Factors for Alzheimer's Disease: Does the Oral Microbiome Hold Some of the Keys?J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;92(4):1111-1129. doi: 10.3233/JAD-220760. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 36872775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral Microbiota Changes in Elderly Patients, an Indicator of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Apr 15;18(8):4211. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18084211. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33921182 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Reciprocal Interactions Between Periodontal Disease and Alzheimer's Disease: Implications for Mutual Triggering, Exacerbation, and Treatment Interventions-A Comprehensive Review of the Literature.Neurol Int. 2025 May 24;17(6):81. doi: 10.3390/neurolint17060081. Neurol Int. 2025. PMID: 40559320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Juglans regia and Pfaffia paniculata extracts: implications for periodontal disease treatment and correlation with Alzheimer's risk.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 May 16;15:1585438. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1585438. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40453709 Free PMC article.
-
Association between periodontal disease and Alzheimer's disease: umbrella review.Front Dent Med. 2025 Jul 9;6:1635200. doi: 10.3389/fdmed.2025.1635200. eCollection 2025. Front Dent Med. 2025. PMID: 40703565 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of light gradient boosting and logistic regression for interactomic hub genes in Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum-induced periodontitis with Alzheimer's disease.Front Oral Health. 2025 Mar 4;6:1463458. doi: 10.3389/froh.2025.1463458. eCollection 2025. Front Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40104076 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Oral Dysbiosis and Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2025 May 13;14(10):3415. doi: 10.3390/jcm14103415. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40429409 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

