Impact of Obesity on Atrial Fibrillation Pathogenesis and Treatment Options
- PMID: 38156451
- PMCID: PMC10863823
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.123.032277
Impact of Obesity on Atrial Fibrillation Pathogenesis and Treatment Options
Abstract
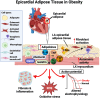
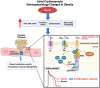
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia. AF increases the risk of stroke, heart failure, dementia, and hospitalization. Obesity significantly increases AF risk, both directly and indirectly, through related conditions, like hypertension, diabetes, and heart failure. Obesity-driven structural and electrical remodeling contribute to AF via several reported mechanisms, including adiposity, inflammation, fibrosis, oxidative stress, ion channel alterations, and autonomic dysfunction. In particular, expanding epicardial adipose tissue during obesity has been suggested as a key driver of AF via paracrine signaling and direct infiltration. Weight loss has been shown to reverse these changes and reduce AF risk and recurrence after ablation. However, studies on how obesity affects pharmacologic or interventional AF treatments are limited. In this review, we discuss mechanisms by which obesity mediates AF and treatment outcomes, aiming to provide insight into obesity-drug interactions and guide personalized treatment for this patient subgroup.
Keywords: antiarrhythmic drugs; atrial fibrillation; epicardial adipose tissue; ion channel; obesity.
Figures


References
-
- Miyasaka Y, Barnes ME, Gersh BJ, Cha SS, Bailey KR, Abhayaratna WP, Seward JB, Tsang TS. Secular trends in incidence of atrial fibrillation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1980 to 2000, and implications on the projections for future prevalence. Circulation. 2006;114:119–125. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.595140 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huxley RR, Lopez FL, Folsom AR, Agarwal SK, Loehr LR, Soliman EZ, Maclehose R, Konety S, Alonso A. Absolute and attributable risks of atrial fibrillation in relation to optimal and borderline risk factors: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Circulation. 2011;123:1501–1508. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.009035 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Obesity and overweight. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2021. Accessed December 09, 2023. https://www.who.int/news‐room/fact‐sheets/detail/obesity‐and‐overweight
-
- Chatterjee NA, Giulianini F, Geelhoed B, Lunetta KL, Misialek JR, Niemeijer MN, Rienstra M, Rose LM, Smith AV, Arking DE, et al. Genetic obesity and the risk of atrial fibrillation: causal estimates from Mendelian randomization. Circulation. 2017;135:741–754. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.024921 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

