A comparative evaluation of the sniffing, the simple head extension and the head hyperextension positions for laryngoscopic view and intubation difficulty in adults undergoing direct laryngoscopy
- PMID: 38157035
- PMCID: PMC10857959
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-023-08386-y
A comparative evaluation of the sniffing, the simple head extension and the head hyperextension positions for laryngoscopic view and intubation difficulty in adults undergoing direct laryngoscopy
Abstract
Objective: This work aimed to compare between the laryngoscopy positions; sniffing, simple head extension and head hyperextension positions to assess whether the laryngeal view, intubation time and intubation difficulty could improve with one of these positions than the others.
Design: Prospective randomized three arms clinical trial.
Setting: Operation room, the phoniatrics unit [removed for blind peer review].
Participants: The study included 75 cases with 25 cases in each group. Group "A" with head in the sniffing position, Group "B" with the head in simple extension position, Group "C" with head in hyperextension position.
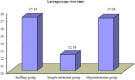
Results: The three groups were compared regarding intubation time and laryngoscopic view time. Intubation time showed statistically significant difference between the three groups. Mean of sniffing group (No. = 25) was 13.19 s (± 3.35). Mean of simple extension group (No. = 25) was 11.29 s (± 3.14). Mean of Hyperextension group (No. = 25) was 14.39 s (± 4.14). Laryngoscopic view time showed statistically highly significant difference between the three groups. Mean of sniffing group (No. = 25) was 17.19 s (± 7.27). Mean of simple group (No. = 25) was 12.18 s (± 4.46). Mean of hyperextension group (No. = 25) was 17.08 s (± 6.51).
Conclusion: Comparing the sniffing, the simple extension and the hyperextension positions, the simple extension position showed the best time regarding intubation time and laryngoscopic view time.
Keywords: Hyperextended position; Laryngeal view; Simple extended position; Sniffing position; Suspension laryngoscopy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest to declare in this study.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Randomized Study Comparing the Sniffing Position with Simple Head Extension for Glottis Visualization and Difficulty in Intubation during Direct Laryngoscopy.Anesth Essays Res. 2017 Jul-Sep;11(3):762-766. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.204206. Anesth Essays Res. 2017. PMID: 28928584 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of direct laryngoscopic views in different head and neck positions in edentulous patients.Am J Emerg Med. 2016 Sep;34(9):1855-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2016.06.011. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Am J Emerg Med. 2016. PMID: 27397669 Clinical Trial.
-
Age and gender are important considerations in choosing the sniffing position for laryngoscopic view.Int J Med Sci. 2014 Oct 2;11(12):1258-61. doi: 10.7150/ijms.8585. eCollection 2014. Int J Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 25317072 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of sniffing position for tracheal intubation: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Am J Emerg Med. 2015 Nov;33(11):1606-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2015.06.049. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Am J Emerg Med. 2015. PMID: 26227445 Review.
-
Ramped versus sniffing position for tracheal intubation: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Am J Emerg Med. 2021 Jun;44:250-256. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.03.058. Epub 2020 Apr 1. Am J Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 32276812
Cited by
-
Influence of Curved Video Laryngoscope Blade Sizes and Patient Heights on Video Laryngoscopic Views: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Pers Med. 2024 Feb 15;14(2):209. doi: 10.3390/jpm14020209. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38392642 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peterson K, Ginglen JG, Desai NM, Guzman N (2018) Direct laryngoscopy - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

