Microbiome profile of the Antarctic clam Laternula elliptica
- PMID: 38157148
- PMCID: PMC10920576
- DOI: 10.1007/s42770-023-01200-1
Microbiome profile of the Antarctic clam Laternula elliptica
Erratum in
-
Correction: Microbiome profile of the Antarctic clam Laternula elliptica.Braz J Microbiol. 2024 Mar;55(1):1031. doi: 10.1007/s42770-024-01254-9. Braz J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38228938 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
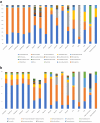
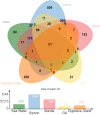
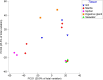
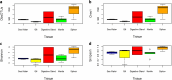
The filter feeder clam Laternula elliptica is a key species in the Antarctic ecosystem. As a stenothermal benthic species, it has a poor capacity for adaptation to small temperature variations. Despite their ecological importance and sensitivity to climate change, studies on their microbiomes are lacking. The goal of this study was to characterize the bacterial communities of L. elliptica and the tissues variability of this microbiome to provide an initial insight of host-microbiota interactions. We investigated the diversity and taxonomic composition of bacterial communities of L. elliptica from five regions of the body using high-throughput 16S rRNA gene sequencing. The results showed that the microbiome of L. elliptica tended to differ from that of the surrounding seawater samples. However, there were no significant differences in the microbial composition between the body sites, and only two OTUs were present in all samples, being considered core microbiome (genus Moritella and Polaribacter). No significant differences were detected in diversity indexes among tissues (mean 626.85 for observed OTUs, 628.89 Chao1, 5.42 Shannon, and 0.87 Simpson). Rarefaction analysis revealed that most tissues reached a plateau of OTU number according to sample increase, with the exception of Siphon samples. Psychromonas and Psychrilyobacter were particularly abundant in L. elliptica whereas Fluviicola dominated seawater and siphons. Typical polar bacteria were Polaribacter, Shewanella, Colwellia, and Moritella. We detected the prevalence of pathogenic bacterial sequences, particularly in the family Arcobacteraceae, Pseudomonadaceae, and Mycoplasmataceae. The prokaryotic diversity was similar among tissues, as well as their taxonomic composition, suggesting a homogeneity of the microbiome along L. elliptica body. The Antarctic clam population can be used to monitor the impact of human activity in areas near Antarctic stations that discharge wastewater.
Keywords: 16S rRNA; Antarctica; Bacteria; Cold-water invertebrates; Filter-feeding.
© 2024. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Sociedade Brasileira de Microbiologia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exposure to nanoplastics and nanomaterials either single and combined affects the gill-associated microbiome of the Antarctic soft-shelled clam Laternula elliptica.Mar Environ Res. 2024 Jun;198:106539. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2024.106539. Epub 2024 May 6. Mar Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 38718522
-
Age-dependent expression of stress and antimicrobial genes in the hemocytes and siphon tissue of the Antarctic bivalve, Laternula elliptica, exposed to injury and starvation.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2014 Jan;19(1):15-32. doi: 10.1007/s12192-013-0431-1. Epub 2013 May 11. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2014. PMID: 23666709 Free PMC article.
-
Complete mitochondrial genome of the Antarctic soft-shelled clam, Laternula elliptica (Bivalvia; Laternulidae).Mitochondrial DNA. 2015 Aug;26(4):642-3. doi: 10.3109/19401736.2013.836515. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Mitochondrial DNA. 2015. PMID: 24083971
-
Heavy metals in sediments and soft tissues of the Antarctic clam Laternula elliptica: more evidence as a possible biomonitor of coastal marine pollution at high latitudes?Sci Total Environ. 2015 Jan 1;502:375-84. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.09.031. Epub 2014 Sep 29. Sci Total Environ. 2015. PMID: 25265398
-
Microbiome Composition and Diversity of the Ice-Dwelling Sea Anemone, Edwardsiella andrillae.Integr Comp Biol. 2016 Oct;56(4):542-55. doi: 10.1093/icb/icw095. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Integr Comp Biol. 2016. PMID: 27493149 Review.
References
-
- Ahn IY. Ecology of the Antarctic bivalve Laternula elliptica (King and Broderip) in Collins harbor, King George Island: benthic environment and adaptative strategy. Mem Natl Inst Polar Res (Tokyo), Spec Issue. 1994;50:1–10.
-
- Pierce ML, Ward JE. Microbial ecology of the Bivalvia, with an emphasis on the Family Ostreidae. J Shellfish Res. 2018;37:793–806. doi: 10.2983/035.037.041. - DOI
-
- Peck L. Ecophysiology of Antarctic marine ectotherms: limits to life. Polar Biol. 2002;25:31–40. doi: 10.1007/s003000100308. - DOI
-
- Peck LS, Webb KE, Bailey DM. Extreme sensitivity of biological function to temperature in Antarctic marine species. Funct. Ecology. 2004;18:625–630. doi: 10.1111/j.0269-8463.2004.00903.x. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

