Quantitative Detection of Biological Nanovesicles in Drops of Saliva Using Microcantilevers
- PMID: 38157306
- PMCID: PMC10788824
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.3c12035
Quantitative Detection of Biological Nanovesicles in Drops of Saliva Using Microcantilevers
Abstract
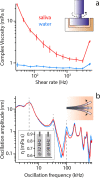
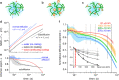
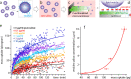
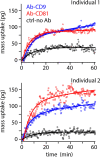
Extracellular nanovesicles (EVs) are lipid-based vesicles secreted by cells and are present in all bodily fluids. They play a central role in communication between distant cells and have been proposed as potential indicators for the early detection of a wide range of diseases, including different types of cancer. However, reliable quantification of a specific subpopulation of EVs remains challenging. The process is typically lengthy and costly and requires purification of relatively large quantities of biopsy samples. Here, we show that microcantilevers operated with sufficiently small vibration amplitudes can successfully quantify a specific subpopulation of EVs directly from a drop (0.1 mL) of unprocessed saliva in less than 20 min. Being a complex fluid, saliva is highly non-Newtonian, normally precluding mechanical sensing. With a combination of standard rheology and microrheology, we demonstrate that the non-Newtonian properties are scale-dependent, enabling microcantilever measurements with a sensitivity identical to that in pure water when operating at the nanoscale. We also address the problem of unwanted sensor biofouling by using a zwitterionic coating, allowing efficient quantification of EVs at concentrations down to 0.1 μg/mL, based on immunorecognition of the EVs' surface proteins. We benchmark the technique on model EVs and illustrate its potential by quantifying populations of natural EVs commonly present in human saliva. The method effectively bypasses the difficulty of targeted detection in non-Newtonian fluids and could be used for various applications, from the detection of EVs and viruses in bodily fluids to the detection of molecular clusters or nanoparticles in other complex fluids.
Keywords: biofouling; cancer; detection; extracellular nanovesicles; microcantilever; microrheology; non-Newtoninan fluid; saliva.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterizing Extracellular Vesicles from Biological Fluids.J Vis Exp. 2025 Feb 28;(216). doi: 10.3791/67699. J Vis Exp. 2025. PMID: 40095994
-
A Novel Capturing Method for Quantification of Extra-Cellular Nanovesicles.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2017 Feb;17(2):908-13. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2017.12631. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2017. PMID: 29671474
-
Efficient EVs separation and detection by an alumina-nanochannel-array-membrane integrated microfluidic chip and an antibody barcode biochip.Anal Chim Acta. 2024 May 22;1304:342576. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2024.342576. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Anal Chim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38637043
-
Methods for loading therapeutics into extracellular vesicles and generating extracellular vesicles mimetic-nanovesicles.Methods. 2020 May 1;177:103-113. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2020.01.001. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Methods. 2020. PMID: 31917274 Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles: A Brief Overview and Its Role in Precision Medicine.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1660:1-14. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7253-1_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28828643 Review.
References
-
- Jameson J. L; Fauci A.; Kasper D. L.; Hauser S. L.; Longo D. L.; Loscalzo J.. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, 20th ed; McGraw Hill, 2018.
-
- Yamamoto C.; Nagashima S.; Isomura M.; Ko K.; Chuon C.; Akita T.; Katayama K.; Woodring J.; Hossain M. S.; Takahashi K.; Tanaka J. Evaluation of the Efficiency of Dried Blood Spot-Based Measurement of Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Virus Seromarkers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10 (1), 3857.10.1038/s41598-020-60703-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li S.; Noor Z. S.; Zeng W.; Stackpole M. L.; Ni X.; Zhou Y.; Yuan Z.; Wong W. H.; Agopian V. G.; Dubinett S. M.; Alber F.; Li W.; Garon E. B.; Zhou J. X. Sensitive Detection of Tumor Mutations from Blood and Its Application to Immunotherapy Prognosis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12 (1), 4172.10.1038/s41467-021-24457-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

