Anakinra or tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with severe covid-19 at high risk of deterioration (IMMCoVA): A randomized, controlled, open-label trial
- PMID: 38157348
- PMCID: PMC10756513
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295838
Anakinra or tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with severe covid-19 at high risk of deterioration (IMMCoVA): A randomized, controlled, open-label trial
Abstract
Background: Anakinra and tocilizumab are used for severe Covid-19, but only one previous randomized controlled trial (RCT) has studied both. We performed a multi-center RCT comparing anakinra or tocilizumab versus usual care (UC) for adults at high risk of deterioration.
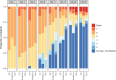
Methods: The study was conducted June 2020 to March 2021. Eligibility required ≥ 5 liters/minute of Oxygen to maintain peripheral oxygen saturation at ≥ 93%, CRP > 70 mg/L, ferritin > 500 μg/L and at least two points where one point was awarded for lymphocytes < 1x 109/L; D-dimer ≥ 0.5 mg/L and; lactate dehydrogenase ≥ 8 microkatal/L. Patients were randomly assigned 1:1:1 to receive either a single dose of tocilizumab (8 mg/kg) or anakinra 100 mg IV QID for seven days or UC alone. The primary outcome was time to recovery.
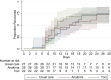
Results: Recruitment was ended prematurely when tocilizumab became part of usual care. Out of a planned 195 patients, 77 had been randomized, 27 to UC, 28 to anakinra and 22 to tocilizumab. Median time to recovery was 15, 15 and 11 days. Rate ratio for recovery for UC vs anakinra was 0.91, 0.47 to 1.78, 95% [CI], p = 0.8 and for UC vs tocilizumab 1.13, 0.55 to 2.30; p = 0.7. There were non-significant trends favoring tocilizumab (and to limited degree anakinra) vs UC for some secondary outcomes. Safety profiles did not differ significantly.
Conclusion: Premature closure of trial precludes firm conclusions. Anakinra or tocilizumab did not significantly shorten time to clinical recovery compared to usual care. (IMMCoVA, NCT04412291, EudraCT: 2020-00174824).
Copyright: © 2023 Sundén-Cullberg et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline. 2022. - PubMed
-
- Kyriazopoulou E, Poulakou G, Milionis H, Metallidis S, Adamis G, Tsiakos K, et al. Early treatment of COVID-19 with anakinra guided by soluble urokinase plasminogen receptor plasma levels: a double-blind, randomized controlled phase 3 trial. Nat Med. 2021;27(10):1752–60. Epub 20210903. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01499-z ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8516650. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martínez-Sanz J, Muriel A, Ron R, Herrera S, Pérez-Molina JA, Moreno S, et al. Effects of tocilizumab on mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a multicentre cohort study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021;27(2):238–43. Epub 20200923. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.09.021 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC7510451. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

