Mechanosensing in Metabolism
- PMID: 38158369
- PMCID: PMC11681368
- DOI: 10.1002/cphy.c230005
Mechanosensing in Metabolism
Abstract
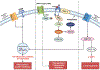
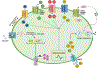
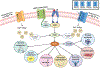
Electrical mechanosensing is a process mediated by specialized ion channels, gated directly or indirectly by mechanical forces, which allows cells to detect and subsequently respond to mechanical stimuli. The activation of mechanosensitive (MS) ion channels, intrinsically gated by mechanical forces, or mechanoresponsive (MR) ion channels, indirectly gated by mechanical forces, results in electrical signaling across lipid bilayers, such as the plasma membrane. While the functions of mechanically gated channels within a sensory context (e.g., proprioception and touch) are well described, there is emerging data demonstrating functions beyond touch and proprioception, including mechanoregulation of intracellular signaling and cellular/systemic metabolism. Both MR and MS ion channel signaling have been shown to contribute to the regulation of metabolic dysfunction, including obesity, insulin resistance, impaired insulin secretion, and inflammation. This review summarizes our current understanding of the contributions of several MS/MR ion channels in cell types implicated in metabolic dysfunction, namely, adipocytes, pancreatic β-cells, hepatocytes, and skeletal muscle cells, and discusses MS/MR ion channels as possible therapeutic targets. © 2024 American Physiological Society. Compr Physiol 14:5269-5290, 2024.
Copyright © 2024 American Physiological Society. All rights reserved.
Figures

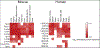
References
-
- Afzali AM, Ruck T, Herrmann AM, Iking J, Sommer C, Kleinschnitz C, Preuße C, Stenzel W, Budde T, Wiendl H, Bittner S, Meuth SG. The potassium channels TASK2 and TREK1 regulate functional differentiation of murine skeletal muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 311 (4): C583–C595, 2016. - PubMed
-
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P. Ion channels and the electrical properties of membranes. In: Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th ed). NY: Garland Science, 2002.
-
- Alghanem AF, Abello J, Maurer JM, Kumar A, Ta C, Gunasekar SK, Fatima U, Kang C, Xie L, Adeola O, Riker M, Elliot-Hudson M, Minerath RA, Grueter CE, Mullins RF, Stratman AN, Sah R. The SWELL1-LRRC8 complex regulates endothelial AKT-eNOS signaling and vascular function. elife 10: e61313, 2021. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ali AT, Hochfeld WE, Myburgh R, Pepper MS. Adipocyte and adipogenesis. Eur J Cell Biol 92 (6–7): 229–236, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Ameer F, Scandiuzzi L, Hasnain S, Kalbacher H, Zaidi N. De novo lipogenesis in health and disease. Metabolism 63 (7): 895–902, 2014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

