NAC61 regulates late- and post-ripening osmotic, oxidative, and biotic stress responses in grapevine
- PMID: 38159048
- PMCID: PMC11016852
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erad507
NAC61 regulates late- and post-ripening osmotic, oxidative, and biotic stress responses in grapevine
Abstract
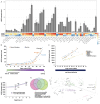
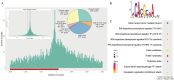
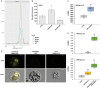
During late- and post-ripening stages, grape berry undergoes profound biochemical and physiological changes whose molecular control is poorly understood. Here, we report the role of NAC61, a grapevine NAC transcription factor, in regulating different processes involved in berry ripening progression. NAC61 is highly expressed during post-harvest berry dehydration and its expression pattern is closely related to sugar concentration. The ectopic expression of NAC61 in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves resulted in low stomatal conductance, high leaf temperature, tissue collapse and a higher relative water content. Transcriptome analysis of grapevine leaves transiently overexpressing NAC61 and DNA affinity purification and sequencing analyses allowed us to narrow down a list of NAC61-regulated genes. Direct regulation of the stilbene synthase regulator MYB14, the osmotic stress-related gene DHN1b, the Botrytis cinerea susceptibility gene WRKY52, and NAC61 itself was validated. We also demonstrate that NAC61 interacts with NAC60, a proposed master regulator of grapevine organ maturation, in the activation of MYB14 and NAC61 expression. Overall, our findings establish NAC61 as a key player in a regulatory network that governs stilbenoid metabolism and osmotic, oxidative, and biotic stress responses that are the hallmark of late- and post-ripening grape stages.
Keywords: Botrytis cinerea; NAC61; Abiotic stress; biotic stress; grapevine; late ripening; post-harvest dehydration; stilbenoid metabolism.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
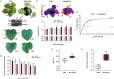



References
-
- Amato A, Cavallini E, Walker AR, et al.. 2019. The MYB5-driven MBW complex recruits a WRKY factor to enhance the expression of targets involved in vacuolar hyper-acidification and trafficking in grapevine. The Plant Journal 99, 1220–1241. - PubMed
-
- Antico CJ, Colon C, Banks T, Ramonell KM.. 2012. Insights into the role of jasmonic acid-mediated defenses against necrotrophic and biotrophic fungal pathogens. Frontiers in Biology 7, 48–56.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

